Fig. 1.
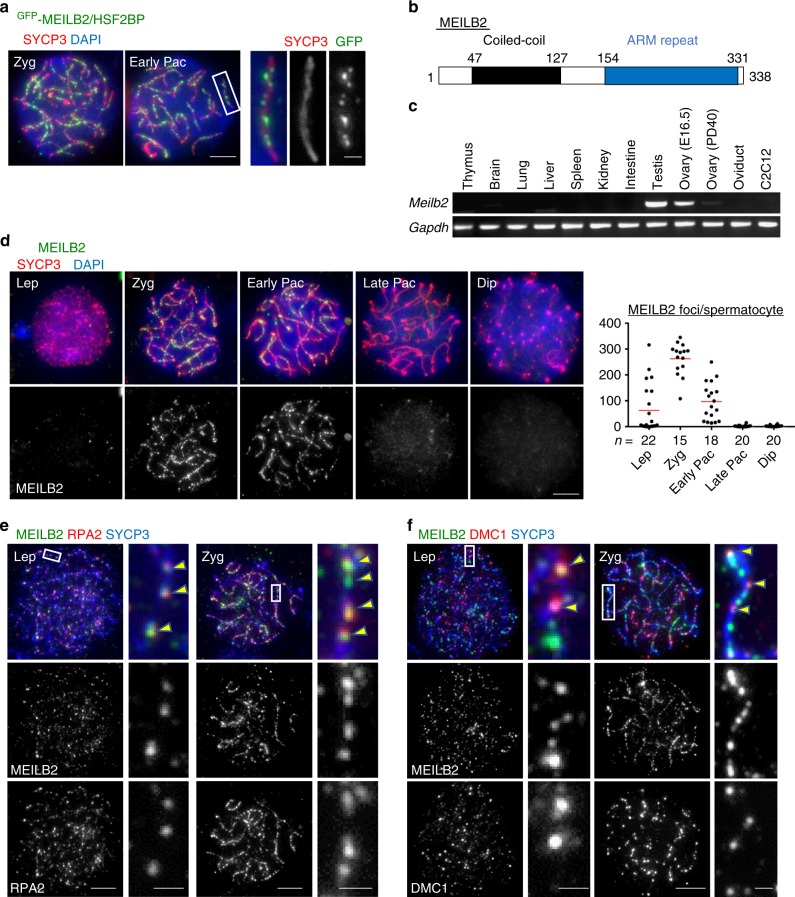
Identification of MEILB2 as a meiotic chromosomal protein. a Wild-type (WT) spermatocytes expressing GFP-MEILB2/HSF2BP stained with the indicated antibodies and 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). b The domain conformation of MEILB2. The coiled-coil domain (a.a. 47–127) and armadillo (ARM) repeat domain (a.a. 154–331) are shown. c Tissue-specific expression levels of Meilb2 and Gapdh (a loading control). C2C12 is a mitotically rounding cancer cell line. d WT spermatocytes stained with the indicated antibodies and DAPI. Each meiotic prophase I substage is shown. The graph shows the number of MEILB2 foci associated with the chromosome axes. The mean value is shown as a red bar. n shows the analyzed spermatocyte number pooled from two mice. Lep leptotene (dotty or discontinuous SYCP3), Zyg zygotene (linear SYCP3 with partial synapsis), Pac pachytene (Early; linear SYCP3 with complete synapsis and Late; linear SYCP3 with complete synapsis and thickened SYCP3 ends), Dip diplotene (linear SYCP3 with desynapsis). e, f WT spermatocytes stained with the indicated antibodies and DAPI. The co-localizing foci along the chromosome axis are highlighted by yellow arrowheads. The quantification of co-localization was performed using three late leptotene cells and six zygotene cells pooled from two mice for RPA2 (e) and six late leptotene cells and ten zygotene cells pooled from three mice for DMC1 (f). The axis-associated foci are counted. Scale bars, 5 and 1 μm (magnified panel). Source data are provided as a Source Data file