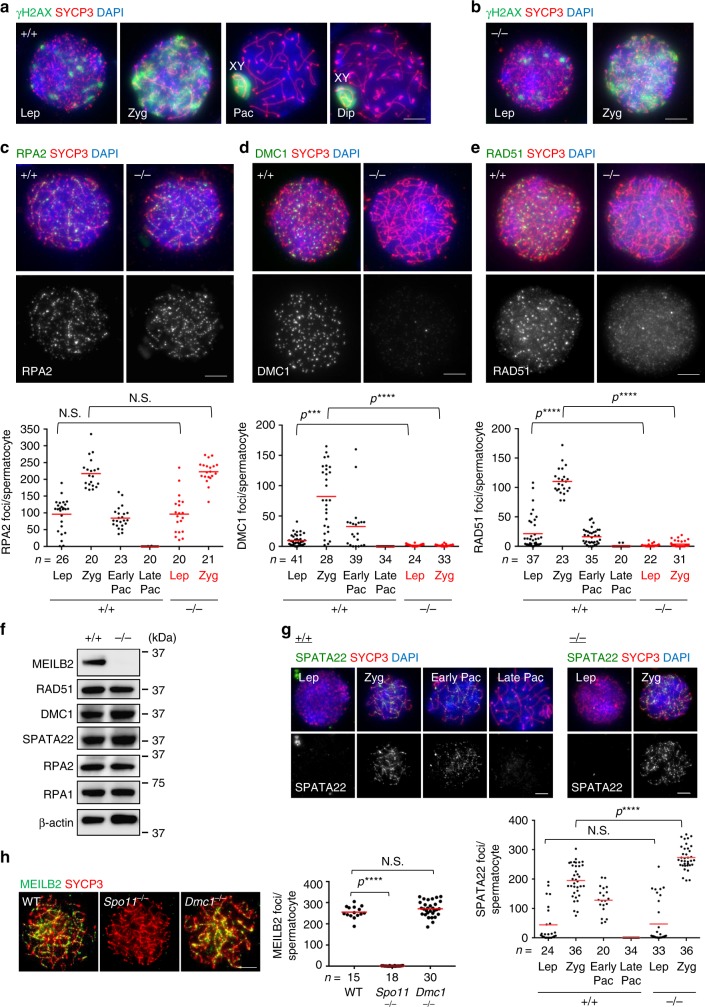
Fig. 4.
DSB repair defects in Meilb2−⁄− male mice. a Spermatocytes from wild-type (WT) (+/+) males stained with the indicated antibodies and 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). b Spermatocytes from Meilb2 knockout (KO) (−/−) males stained with the indicated antibodies and DAPI. c–e Zygotene spermatocytes from WT (+/+) and Meilb2 KO (−/−) males stained with SYCP3 in red, DAPI in blue, and RPA2 (c), DMC1 (d), or RAD51 (e) in green. The images in the other stages are shown in Supplementary Figs. 4d and 5a. The graph shows the number of RPA2 (c), DMC1 (d), or RAD51 (e) foci associated with the chromosome axes. The mean value is shown as a red bar. n shows the analyzed spermatocyte number pooled from three mice for each genotype. f Immunoblots of mouse testis extracts (PD90) from WT (+/+) and Meilb2 KO (−/−) males using the indicated antibodies. g Spermatocytes from WT (+/+) and Meilb2 KO (−/−) males stained with the indicated antibodies and DAPI. Each meiotic prophase I substage is shown. The graph shows the number of SPATA22 foci associated with the chromosome axes. The mean value is shown as a red bar. n shows the analyzed spermatocyte number pooled from four mice for each genotype. h Zygotene spermatocytes from WT, Spo11−⁄−, and Dmc1−⁄− males stained with the indicated antibodies and DAPI. The graph shows the number of MEILB2 foci associated with the chromosome axes in zygotene spermatocytes. The mean value is shown as a red bar. n shows the analyzed spermatocyte number pooled from two mice for each genotype. Lep leptotene, Zyg zygotene, Pac pachytene, Dip diplotene. All analyses were with two-tailed t tests. N.S. not significant. ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Scale bars, 5 μm. Source data are provided as a Source Data file