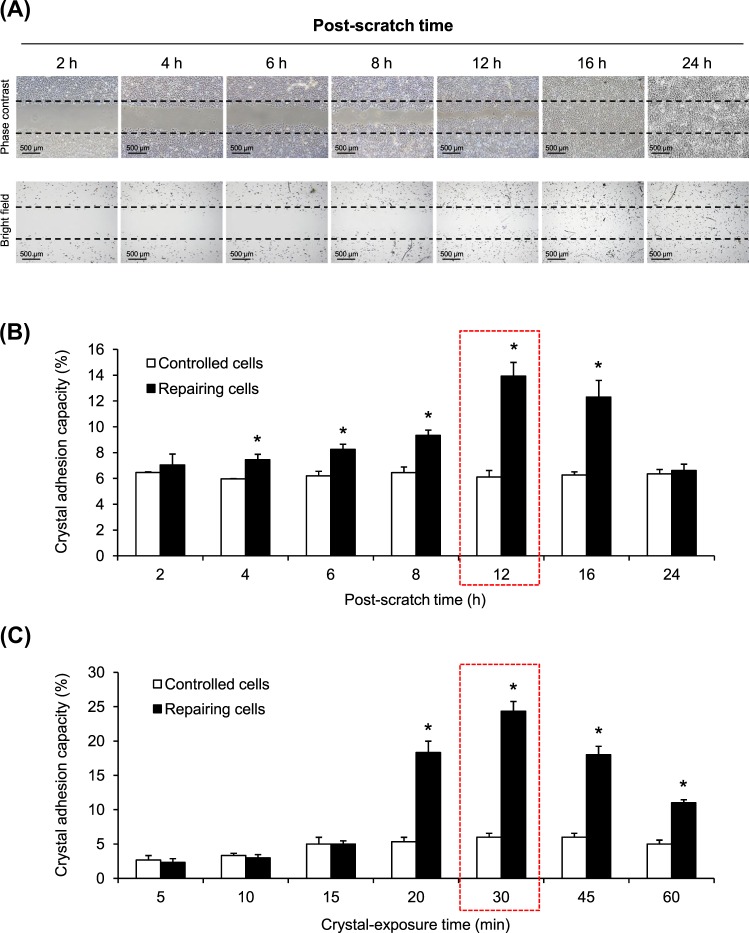
Fig. 1. Optimization of crystal-cell adhesion assay to evaluate repairing cells.
a Multiple mesh-like scratches were made on MDCK confluent monolayer to generate repairing cells, whereas the non-scratched monolayer served as the control. At 2-, 4-, 6-, 8-, 12-, 16-, and 24-h post-scratch, crystal adhesion assay was performed with a fixed crystal-exposure time at 60 min following the standard protocol. Micrographs were taken by using a phase contrast microscope (original magnification = ×40 in all panels). b Crystal adhesion capacity of the cells was examined from at least 15 randomized high-power fields (HPFs) in each well. c Crystal-cell adhesion assay was performed at a fixed post-scratch time-point (12 h), whereas crystal-exposure time was varied at 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 45, and 60 min. Each bar represents mean ± SEM of the data obtained from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 vs. control