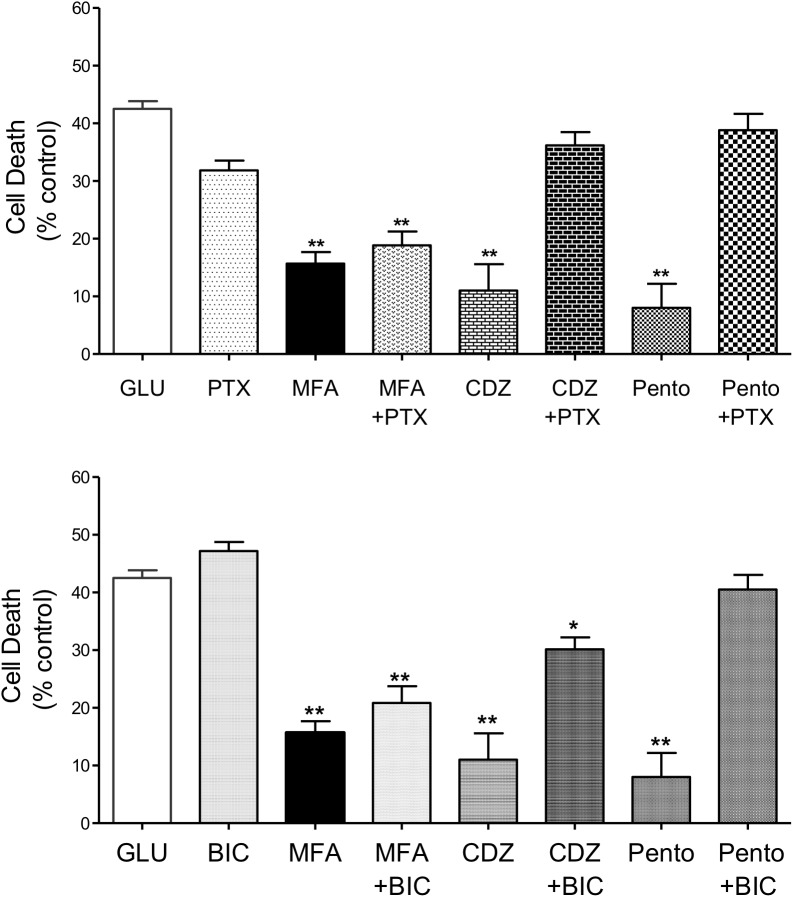
FIGURE 6.
Impact of GABAA receptor and ion channel inhibition on the neuroprotective effects of MFA in vitro: hippocampal neurons cultured for 9 days were exposed to glutamate (5 μM) and test drugs by co-incubating during exposure and immediately after exposure for 24 h. Cell death was quantified using Cytotox-96 at 24 h post-exposure. (Top) Treatment with MFA (100 μM), chlordiazepoxide (CDZ, 100 μM), or sodium pentobarbital (Pento, 100 μM) reduced glutamate induced cell death by 62, 74, and 81% (∗∗p ≤ 0.01) respectively. Picrotoxin (PTX, 100 μM) abolished the neuroprotective effect of CDZ and sodium pentobarbital on glutamate-evoked cell death but did not significantly alter the action of MFA. Picrotoxin (100 μM) alone did not reduce glutamate evoked cell death. (Bottom) MFA, CDZ or pentobarbital (all tested at 100 μM) reduced glutamate induced cell death by 62, 74, and 81% (∗∗p ≤ 0.01) respectively. Bicuculline (BIC, 10 μM) abolished the effect of pentobarbital and significantly reduced the neuroprotective effect of CDZ on glutamate induced cell death, but failed to alter the effect of MFA. Bicuculline (10 μM) alone did not reduce glutamate evoked cell death ∗p < 0.05.