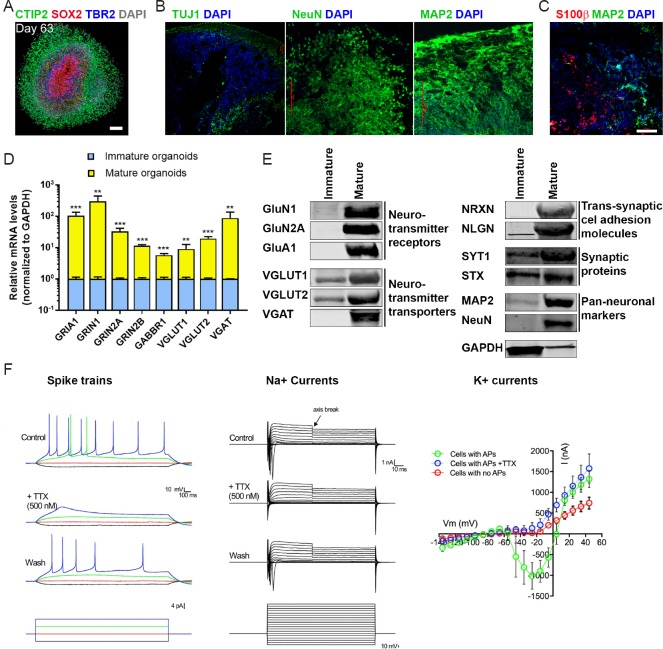
Figure 1.
Optimal cerebral organoids recapitulate the structure, gene expression profiles and electrophysiological properties of the human brain.
(A) An example organoid on day 63 post-differentiation immunohistochemically stained, showing a multi-layer structure encompassing SOX2+ neural progenitor cells, TBR2+ intermediate progenitor cells, and CTIP2+ neurons; scale bar: 100 μm; adapted, with permission, from Qian et al. (2016). (B) Three sections from H1-derived organoids were stained with TUJ1, NeuN or MAP2, and DAPI and imaged using confocal microscopy; scale bar: 100 μm; adapted, with permission, from Yakoub and Sadek (2018). (C) An organoid section was stained with S100β and MAP2 and imaged using confocal microscopy; scale bar: 100 μm; adapted, with permission, from Yakoub and Sadek (2018). (D) qPCR analysis of mature-neuron markers in organoids on day 35 post-differentiation (“mature”), compared to the day-0 (“immature”) stage. Relative mRNA levels were calculated and normalized to the housekeeping gene GAPDH; error bars: SD; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (Student’s t-test). (E) Immunoblotting analysis of mature-neuron markers in 44-day old (“mature”), relative to day 0 (“immature”), organoids; adapted, with permission, from Yakoub and Sadek (2018). (F) Electrophysiological recordings from organoid slices. Left panel shows representative spike trains upon current stimulation in the absence (control) or presence of the sodium channel blocker TTX (n = 12 out of 24 cells showed action potentials (APs)). Middle panel shows TTX-sensitive sodium currents. Right panel shows potassium currents in the cells without or with APs, or with APs in presence of TTX. The left, middle, and right panels were adapted, with permission, from Watanabe et al. (2017). SOX2: Sex determining region Y-box 2; TBR2: T-box brain protein 2; DAPI: 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; TUJ1: neuron-specific class III β-tubulin; MAP2: microtubule-associated protein 2; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; SD: standard deviation; TTX: tetrodotoxin; CTIP2: (chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor)-interacting protein 2; GluN1: glutamate ionotropic receptor NMDA-type subunit 1 (encoded by the gene GRIN1); GluN2A: glutamate ionotropic receptor NMDA-type subunit 2A (encoded by the gene GRIN2A); GluA1: glutamate ionotropic receptor AMPA-type subunit 1 (encoded by the gene GRIA1); VGLUT1: vesicular glutamate transporter 1; VGLUT2: vesicular glutamate transporter 2; VGAT: vesicular γ-amino butyric acid transporter; NRXN: neurexin; NLGN: neuroligin; SYT1: synaptotagmin 1; STX: syntaxin; S100β: S100 calcium-binding protein-β.