Figure 1.
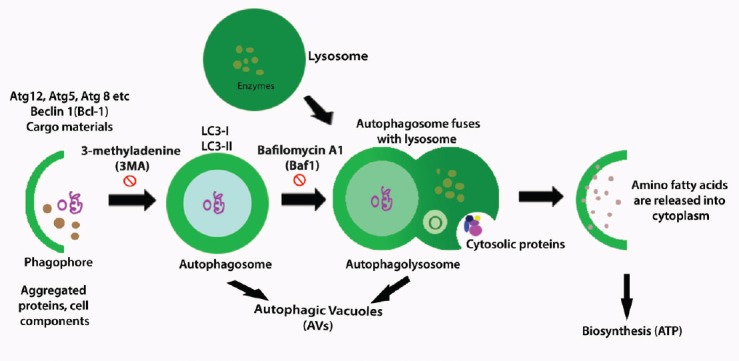
General process of autophagy.
At the begining of this process, cup-shaped phagophore is formed around the folded or aggregated proteins and with other cellular components, this is called nucleation. In the first step, the autophagic proteins (Atgs) such as Atg12, Atg 5, Atg 8, Beclin-1 (Bcl-1) and cargo materials are brought about through the ubiquitin-like conjugation systems Atg12-Atg5-Atg16L and Atg8 (LC3)-phosphatidylethanolamine (PE). In the second step, the expansion and maturation of the cup-shaped structure become rounded one and form autophagolysosomes which are double membraned vesicles with presence of LC3-I, LC3-II where the 3-methyladenine (3-MA) plays an inhibitatory role. In the third step, with an inhibitiory effect of bafilomycin A1 (Baf1), autophagosome is fused with lysosome and form single membraned autophagolysosome and this step is called fusion and autophagic vacuoles (AVs) and cytosolic proteins are seen. In the last step, the degradation of the autophagolysosome, with hyrolytic enzymes contributes to degradation of sequestered material, release of amino or fatty acids, and maintaineance of biogenesis.
