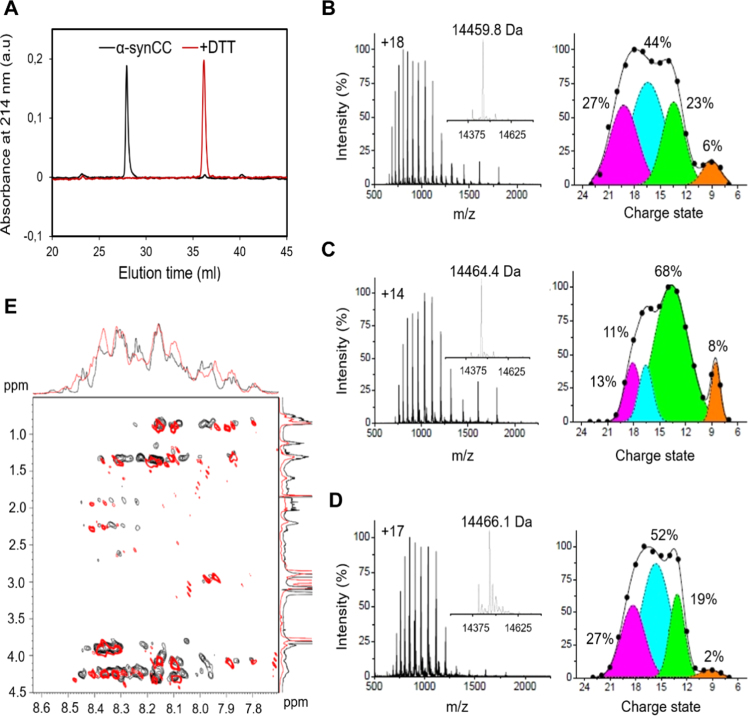
Fig. 3.
α-synCC disulfide formation induces compactness. (A) RP-HPLC elution profile of α-synCC before (black) and after reduction with DTT (red). (B-D) ESI-MS analysis showing the conformational ensembles of wt α-syn and α-synCC. ESI-MS spectra and Gaussian fits of the charge-state distributions obtained using 4 conformers (orange - compact conformer; green - compact intermediate state; cyan - extended intermediate state; magenta - fully extended conformer) for wt α-syn (B), oxidized α-synCC (C) and reduced α-synCC (D) are shown. The most intense peak of each ESI-MS spectra is labelled by the corresponding charge state. Inserts report the mass-deconvolution spectrum. Each Gaussian component is labelled by its relative amount in percentage. (E) 2D-TOCSY 1H–1H NMR-spectrum of wt α-syn (black) and α-synCC (red) dissolved in 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.4 at 25 °C.