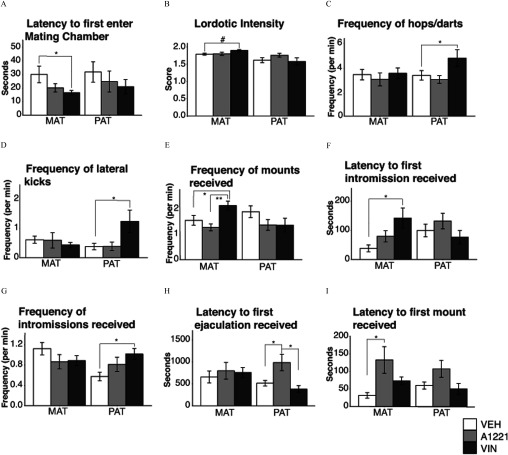
Figure 9.
Females were observed for sexual behavior in a paced mating chamber. Latency to first enter the (A) mating chamber, (B) lordotic intensity, (C) frequency of hops/darts, (D) frequency of lateral kicks to males, (E) frequency of mounts received, (F) latency to receive a first intromission, (G) frequency of intromissions, (H) latency to first ejaculation, and (I) latency to first mount are shown as . Note: A1221, Aroclor 1,221; MAT, maternal; PAT, paternal; VEH, vehicle; VIN, vinclozolin. #; *; ** as determined by analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s HSD posthoc analysis.