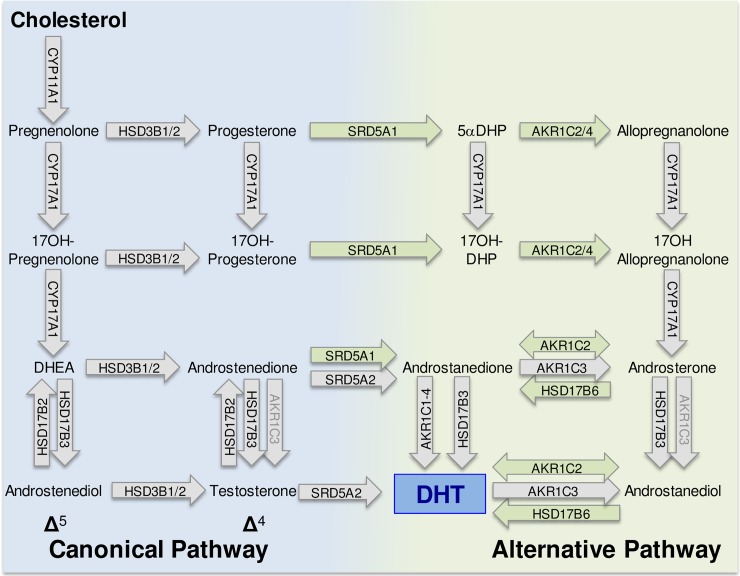
Fig 1. Canonical and alternative (backdoor) pathways of DHT synthesis.
The canonical pathway has potential Δ4 and Δ5 subpathways. The enzymes that catalyze each step are indicated within the arrows. Enzymes written in black on a gray arrow are essential components of the canonical pathway, and some appear in both canonical and backdoor pathways (e.g., CYP17A1). Enzymes written in black on a green background are specific to the backdoor pathway. Enzymes in gray text will carry out the described conversion, but they may not be the principal enzyme involved. Other enzymes, not shown, may also be involved in components of the backdoor pathway [17]. Human CYP17A1 can convert progesterone to 17α-hydroxyprogesterone, but 17–20 lyase activity is very low with 17α-hydroxyprogesterone as substrate, and significant androstenedione is not produced by the Δ4 pathway in humans [18]. Similarly, 17OHDHP is a poor substrate for 17–20 lyase activity [19]. androstanediol, 5α-androstan-3α, 17β-diol; androstanedione, 5α-androstane-3,17-dione; androstenediol, androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol; DHEA, dehydroepiandrosterone; DHT, dihydrotestosterone; 5αDHP, 5α-dihydroprogesterone; 17OHDHP, 17α-hydroxydihydroprogesterone.