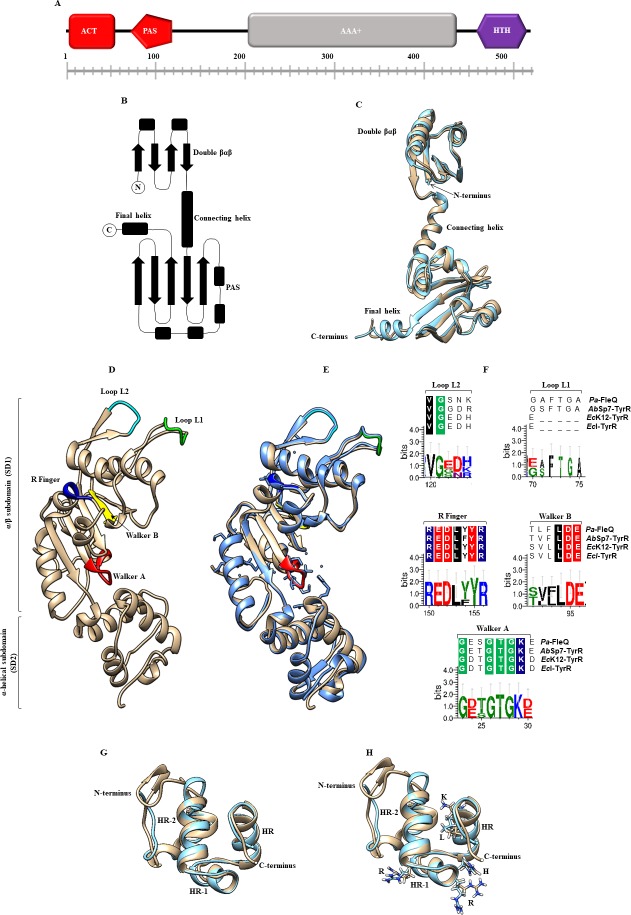
Fig 1. The overall predicted and domains displayed by the TyrR protein from A. brasilense Sp7 (Ab-Sp7).
(A) The TyrR protein consists of an ACT domain (red square), a PAS domain (red pentagon), an AAA+ domain (gray rectangle) and an HTH motif (purple hexagon). (B) The topology of the N-terminal region of a TyrR monomer from E. coli K12 with its separate domains. (C) Comparison by superposition of monomers of TyrR from the E. coli K12 (blue) crystal structure with a resolution of 2.3 Å and Ab-Sp7 (beige) with a root mean square deviation (RMSD) of 1.59 Å. (D) The prediction of the AAA+ monomer domain of TyrR from Ab-Sp7. The ribbon representation of Ab_TyrR-AAA+ consists of an α/β sub domain followed by a smaller α-helical subdomain. The regions and the PAS domain are highlighted. (E) Superimposition of the Pa_FleQ-AAA+ crystal structure with a resolution of 1.8 Å (blue) and Ab_TyrR-AAA+ (beige) with a RSMD of 0.89 Å. The significant motifs are highlighted: Walker A (red), Walker B (yellow), R finger (dark blue), Loop L1, (green), Loop L2 (cyan). (F) Sequence logo representations of sequence alignments of Walker A (GXXXXGK), Walker B (hhhhDE), R finger (RXXXXXR), Loop L2 (VG), Loop L1 (GAFTGA), and multiple sequence alignments of FleQ (P. aeruginosa), TyrR (A. brasilense Sp7), TyrR (E. coli K12), TyrR (E. cloacae) were used. (G) Comparison by structure superimposition of the Ab-TyrR-HTH model (beige) and template 1G2H of H. influenzae (blue color). Three well defined α-helices (HR-2, HR-1, and HR) are shown. (H) Superimposed structures show the crucial amino acids involved in forming hydrogen bonds directly with DNA are highlighted: arginine 291 (R), arginine 296 (R), histidine 301 (H), lysine 307 (K), and leucine 308 (L). The homology models constructed by I-Tasser with the best scores, C-score -1.21, RMSD 1.25 Å, visualized with UCSF Chimera software. Logos were generated with the Weblogo 3 Create software.