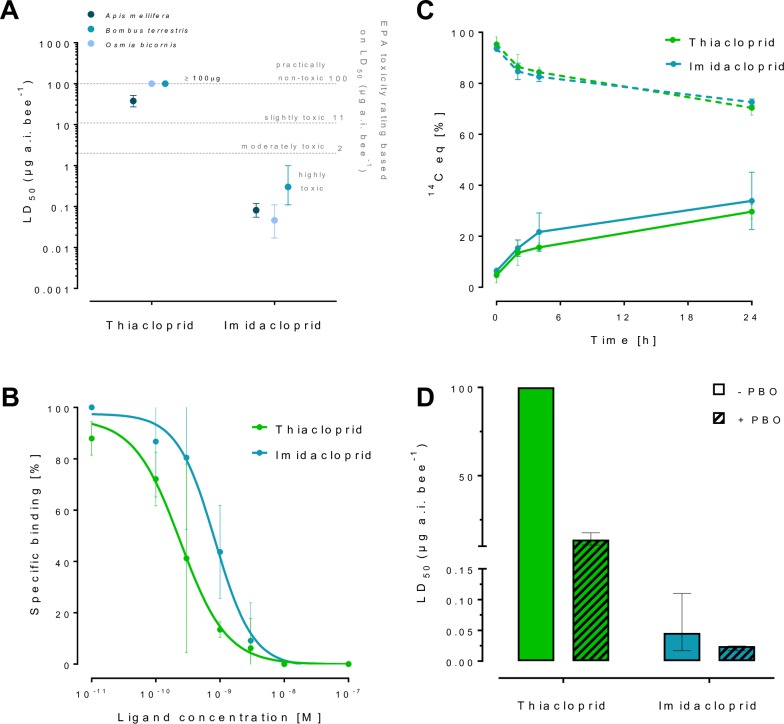
Fig 2. Toxicodynamics and pharmacokinetics of neonicotinoid sensitivity in O. bicornis.
(A) LD50 values for imidacloprid and thiacloprid in insecticide bioassays for O. bicornis, for comparison data is also shown for A. mellifera and B. terrestris. Sensitivity thresholds are depicted according to EPA toxicity ratings [45]. Data for A. mellifera is taken from [13,14], data for B. terrestris is taken from [3]. Error bars display 95% CLs (n = 4). (B) Specific binding of thiacloprid and imidacloprid to O. bicornis nAChRs. Error bars display standard deviation (n = 3). (C) Penetration of radiolabelled thiacloprid and imidacloprid through the cuticle of O. bicornis. The percentage of the initial 14C-imidacloprid and 14C-thiacloprid dose recovered by external cuticular rinsing over 24 hours is shown by dashed lines. The percentage of 14C-imidacloprid and 14C-thiacloprid recovered from combusted bees (i.e. internalized compound) is shown by solid lines. Error bars display standard deviation (n = 3). (D) Sensitivity of O. bicornis to imidacloprid and thiacloprid before and after pre-treatment with the insecticide synergist PBO (piperonyl butoxide). Error bars display 95% CLs (n = 3).