Figure 6:
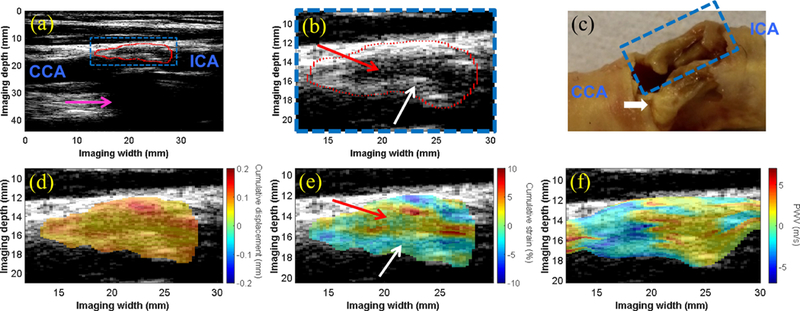
(a) The B-mode image of the carotid bifurcation in a 75-y.o. male shows the plaque (red contour) situated at the bifurcation and extending into the proximal ICA. Acoustic shadowing (pink arrow) is observed. (b) An enlarged image of the plaque ROI (blue box in a) shows an echolucent region (red arrow) surrounded by an echogenic border indicative of the fibrous cap (white arrow). (c) Gross pathology reveals bilateral plaques with liquid-like fatty substance oozing from the plaque of interest (blue dashed box). The white calcified nodule (yellow) in the far wall plaque is likely the main contributor to the acoustic shadowing observed in (a). The intra-plaque cumulative displacement map (d) is mostly uniform, while the cumulative strain map (e) reveals compression in the solid fibrous cap (white arrow) and elongation in the liquid-like fatty region (red arrow). The intra-plaque PWV map (f) revealed a transition from negative PWV to positive PWV in the direction of wave propagation at all depths of the plaque.
