Figure 3.
BET BRDs Initiate Interactions with Non-histone Kac-XX-Kac Peptides
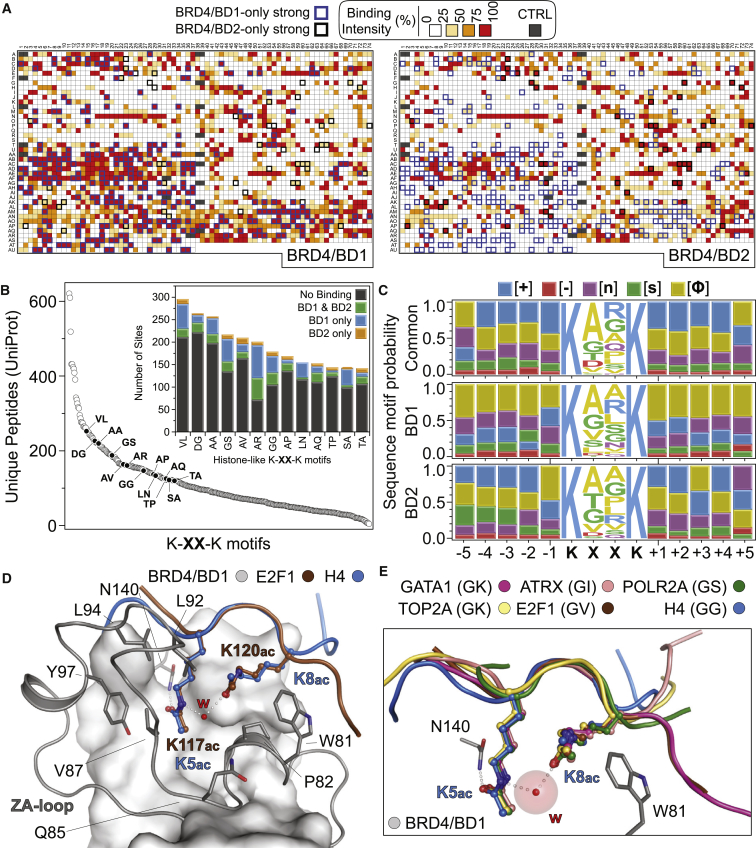
(A) Peptide SPOT validation of histone-like peptides containing a Kac-XX-Kac motif. The heatmap shows binding intensities against the first (BD1) and second (BD2) BRDs of BRD4. Peptides exhibiting strong (≥75% of maximum) intensity toward one domain, with a ≥2-fold lower intensity toward the other domain are highlighted.
(B) Unique peptides containing K-XX-K motifs found in the human proteome. The inset highlights the binding results from (A) toward BRD4 BRDs.
(C) Peptide LOGOs derived from very strong (≥85% of maximum intensity) binding in the SPOT arrays shown in (A).
(D) Crystal structure of BRD4/BD1 bound to an E2F1 di-Kac peptide (K117ac-XX-K120ac motif) or the previously published histone H4 K5ac/K8ac peptide (PDB: 3UVW).
(E) Structural overlay of BRD4/BD1 complexes with Kac-GX-Kac-bearing peptides shown in cartoon, highlighting the topology of the BRD cavity with respect to the conserved asparagine (N140) and the bulky tryptophan of the WPF shelf (W81).