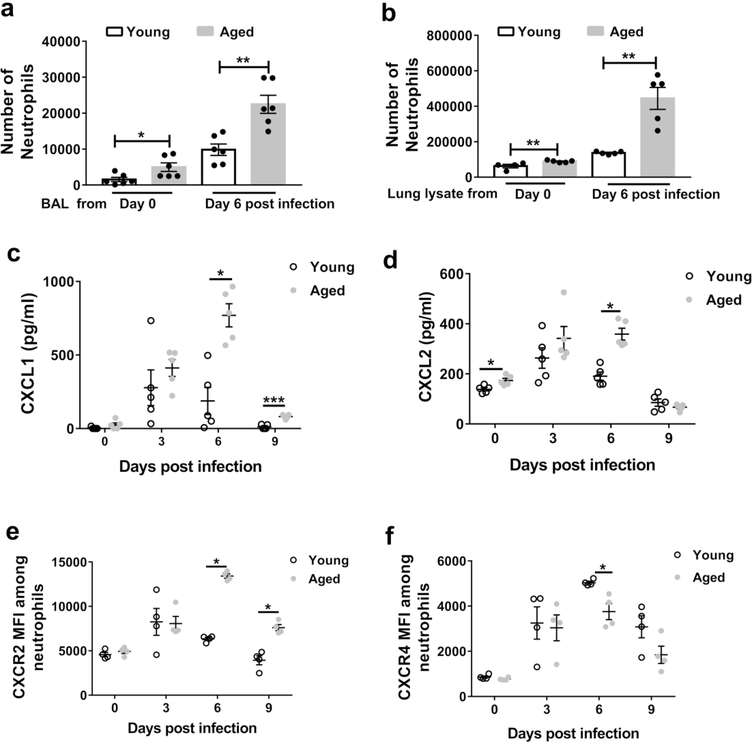
Figure 5. Aging increases the levels of CXCL1 and CXCL2 in lung during influenza infection and enhances neutrophil chemotaxis in vitro.
a-b Bone marrow neutrophils were purified from young non-infected mice and added to chemotaxis assays in which the chemoattractant was either the BAL (a) or lung lysate (b) of non-infected or infected (day 6 post-infection), young and aged mice. Young neutrophils exhibited a significant increased chemotaxis towards the fluid obtained from the lungs of aged mice than young mice (before or after infection) * P < 0.05 ** P < 0.01 (Mann-Whitney test). c-d BAL was obtained during the course of influenza infection in young and aged mice and CXCL1 (c) and CXCL2 (d) measured within the BAL via ELISA. n = 5/ time point / group. * P < 0.05 *** P < 0.001 (Mann-Whitney test).
e-f Surface expression of CXCR2 and CXCR4 on neutrophils in the lung before and during the course of influenza infection in young and aged mice. n = 4/ time point / group. * P < 0.05 (Mann-Whitney test).