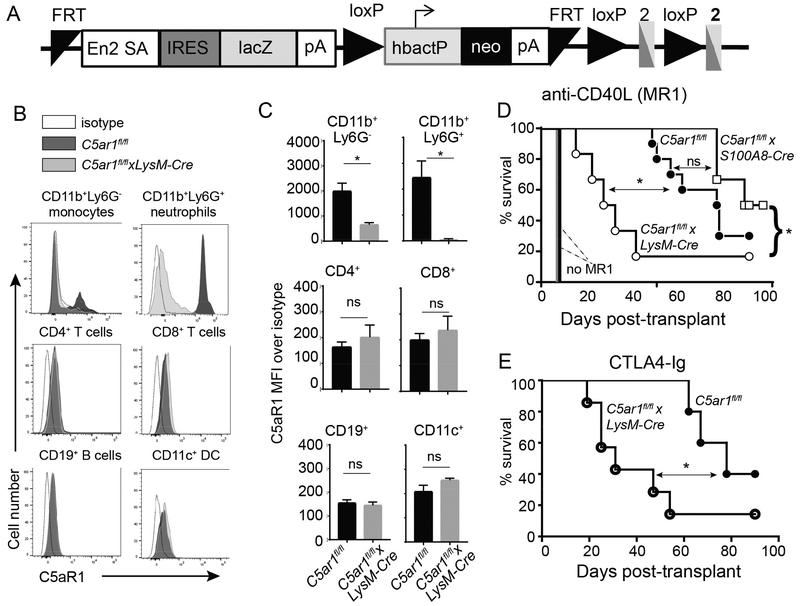
Figure 1.
Myeloid cell deficiency of C5ar1 abrogates costimulatory blockade induced prolonged cardiac allograft survival. A. Schematic representation of the targeting insert to conditionally delete C5ar1. Animals transmitting the insert were crossed with flp/flp mice to remove the genes between the 2 FRT sites. The resultant C5ar1fl/fl mice were crossed to a LysM-Cre transgenic to remove a portion of C5ar1 exon 2 from myeloid cells or to an S100A8-Cre transgenic to remove a portion of C5ar1 exon 2 from neutrophils. B-C. Representative flow cytometry plots (B) and quantified surface expression (MFI) of C5aR1 (C) on monocytes and neutrophils (top row) CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (middle row), and B cells and DCs (bottom row). D. Survival of BALB/c hearts transplanted into C5ar1fl/fl, C5arfl/flxLysM-Cre or C5arfl/flxS100A8-Cre recipients treated with anti-CD40L mAb MR1 250μg on day −1 (n=6–10/group). Survival of BALB/c hearts in untreated C5ar1fl/fl (solid black line, no symbol) and C5arfl/flxLysM-Cre (solid gray line, no symbol, n=4/group) recipients. E. Survival of BALB/c hearts transplanted into C5ar1fl/fl or C5arfl/flxLysM-Cre and treated with CTLA4-Ig (n=5–7/group) (E). *p<0.05 by t-test. ns: nonsignificant. *p<0.05, **p<0.05 by survival analysis (Mantel-Cox log rank test). ns=not significant.