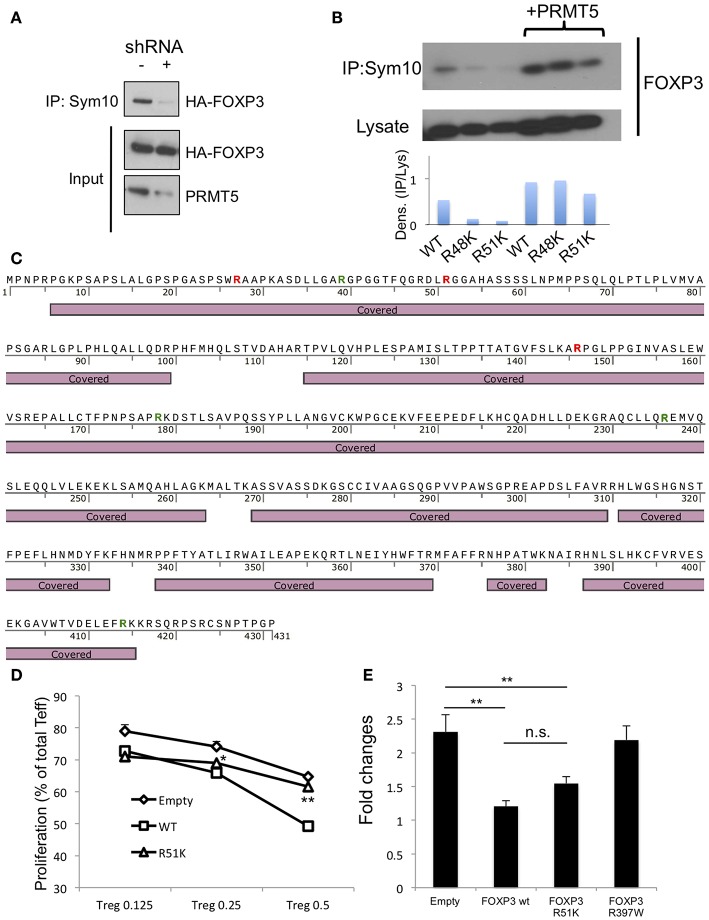
Figure 5.
Analysis of methylation sites in human FOXP3. (A) symmetrical methylation of FOXP3. 293T cells were transfected with FOXP3 and empty or PRMT5 shRNA86 vector. After 24 h of transfection, the cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-sym10, which recognizes symmetrical arginine dimethylation, and then subjected to western blotting. (B) symmetrical methylation analysis of human FOXP3 wild type (WT), R48K and R51K mutant in 293T systems. (C) methylation analysis of FOXP3 by mass spectrometry. HA-FOXP3 transfected 293T cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-HA beads, then subjected for mass spectrometry. Covered: FOXP3 sequences detected by mass spectrometry. Red letters show the arginine that is di-methylated. Green letters show the arginine that is mono-methylated. (D) suppressive functions of FOXP3 R51K. Human CD4+ T cells were transfected with empty, FOXP3 WT and FOXP3 R51K mutant, then used as suppressors in the suppression assay. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 with FOXP3 WT groups calculated by student t-test. (E) IL-2 promoter assay with FOXP3-transfected Jurkat cells. Jurkat cells were transfected with the IL-2 promoter vector and additional indicated vectors. Twenty four hours after transfection, cells were transferred to 24 wells (250 μl/well), stimulated with PMA and ionomycin for 6 h, and then subjected to the luciferase assay. The error bars indicate the SD value. **P < 0.01 with control vehicle groups calculated by one way ANOVA with Tukey HSD test.