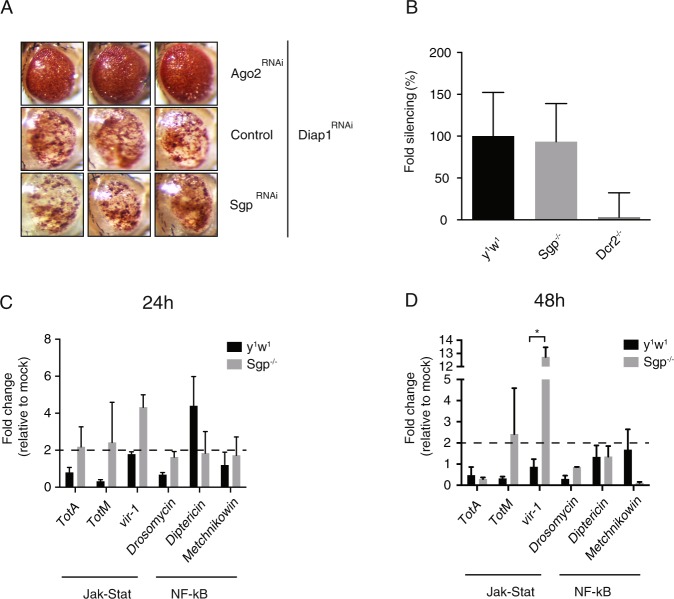
Figure 3.
RNAi and canonical immune pathways are functional in Sgroppino mutants. (A) Eye phenotype of 5 to 7-day-old flies expressing a hairpin RNA targeting the Death-associated inhibitor of apoptosis Diap1 (Diap1RNAi), combined with either a hairpin RNA targeting Ago2 (Ago2RNAi), a hairpin targeting Sgp (SgpRNAi), or the genetic background of the SgpRNAi line (control). Wild-type eye phenotype was observed in flies not expressing the Diap1RNAi transgene from the same cross. Three representative images are shown for each genotype. (B) In vivo RNAi reporter assay. Firefly (Fluc) and Renilla (Ren) luciferase reporter plasmids were co-transfected with Fluc specific dsRNA or non-specific control dsRNA in Sgp and Dcr2−/− mutant flies and wild-type control flies (y1w1). Fold silencing by Fluc dsRNA relative to control dsRNA was calculated and presented as percentage of wild-type controls. Data are means and s.d. of three independent pools of 5 female flies for each genotype. (C,D) Expression of immune genes at (C) 24 and (D) 48 hours after DCV infection (inoculum of 10,000 TCID50) determined by RT-qPCR in wild-type or Sgp mutant flies. Expression of the indicated genes was normalized to transcript levels of the housekeeping gene Ribosomal Protein 49 and expressed as fold change relative to mock infection (Tris buffer). Data are means and s.d. of three independent pools of 10 female flies for each genotype. *P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test).