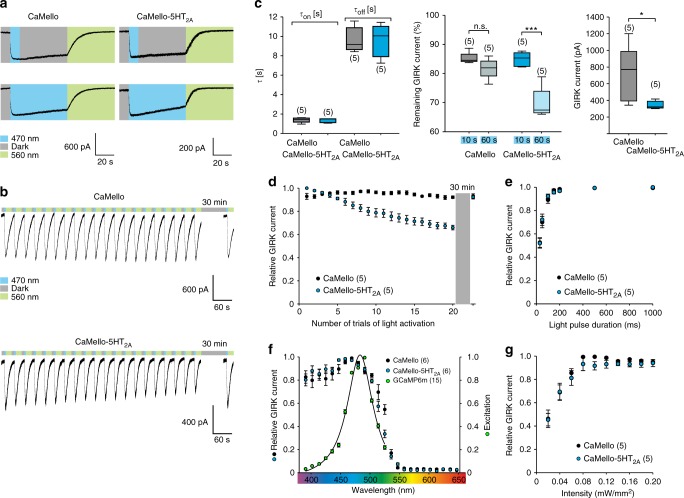
Fig. 2.
Electrophysiological characterization of CaMello and CaMello-5HT2A. a Whole-cell patch clamp recordings of light-induced GIRK currents in HEK GIRK 1/2 cells activated and subsequently deactivated via CaMello or CaMello-5HT2A using a 10 s light pulse with a 50 s dark phase (top) or a 60 s light pulse (bottom) of 470 nm for activation followed by a 50 s light pulse of 560 nm for deactivation. b Repetitive activation/deactivation of GIRK currents via CaMello or CaMello-5HT2A followed by a 30 min dark phase and an additional activation/deactivation. c Time constants of GIRK current activation/deactivation by CaMello/CaMello-5HT2A using 10/50 s light pulses of 470/560 nm (left). Remaining GIRK current after 60 s of recording following 10 or 60 s of 470 nm light stimulation for CaMello/CaMello-5HT2A (middle). Maximal induced GIRK current amplitude for CaMello/CaMello-5HT2A using a 10 s light pulse of 470 nm (right) (box plot; one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Holm-Sidak multiple comparison method or Mann–Whitney rank sum test; n = 5 individual cells recorded; n.s. = not significant, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001; p left to right: 0.889, < 0.001, 0.032). d Relative GIRK current response during repetitive light stimulation as shown in (b). e Light-pulse duration dependence of relative GIRK current activation by CaMello/CaMello-5HT2A using a 470 nm light pulse of the indicated duration for activation followed by a 560 nm light pulse for deactivation. f Wavelength dependence of relative GIRK current activation via CaMello/CaMello-5HT2A using a 1 s light pulse of the indicated wavelength for activation followed by a 560 nm light pulse for deactivation. The superimposed (CaMello-)GCaMP6m excitation spectrum was measured via 1 s 470 nm activation of CaMello followed by fluorescence emission recording (530–550 nm) for each indicated excitation wavelength (390–520 nm). g Intensity dependence of relative GIRK current activation via CaMello/CaMello-5HT2A using a 1 s 470 nm light pulse of the indicated intensity for activation followed by a 560 nm light pulse for deactivation after each activation. Plotted data (d–g) presented as mean (± s.e.m); n = number of individual cells recorded