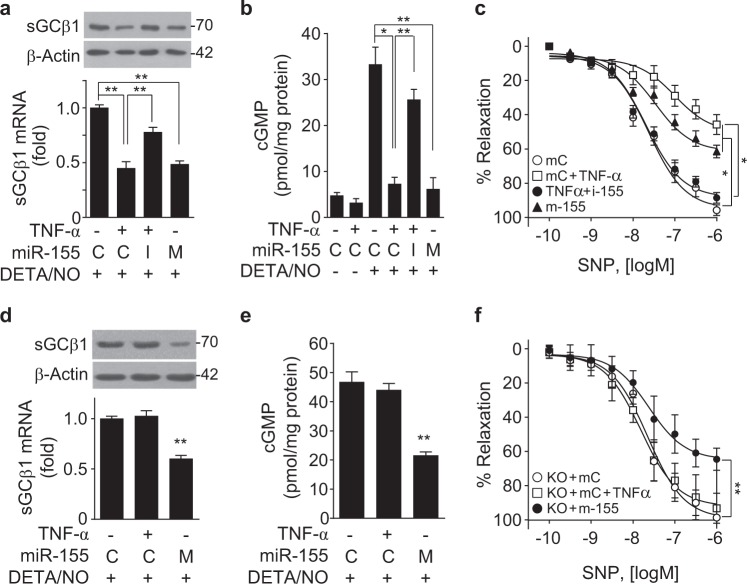
Fig. 6. MiR-155 suppresses vasorelaxation by inhibiting the sGC/cGMP pathway.
a Mouse de-endothelialized aortic rings were transfected with 100 nM of control miRNA (C), miR-155 mimic (M), or miR-155 inhibitor (I), followed by treatment with or without TNF-α (20 ng/mL) for 24 h. The sGCβ1 mRNA and protein levels were determined by qRT-PCR (n = 3) and Western blotting. b De-endothelialized aortic rings were transfected with miR-155 mimic and miR-155 inhibitor and stimulated with or without TNF-α for 24 h, followed by treatment with DETA/NO for another 24 h. The cGMP levels were determined in vessel lysates using a cGMP assay kit (n = 3). c De-endothelialized aortic rings were transfected with control miRNA, miR-155 mimic (m-155), or miR-155 inhibitor (i-155), followed by treatment with TNF-α for 24 h. The cumulative vascular relaxation response of the aortic rings to SNP was measured by myography (n = 8). d–f De-endothelialized aortic rings from miR-155−/− (KO) mice were transfected with 100 nM of control miRNA (C, mC) or miR-155 mimic (M, m-155) and stimulated with or without TNF-α for 24 h, followed by treatment with DETA/NO (100 μM) for another 24 h. d The sGCβ1 mRNA levels were determined (n = 5). e The cGMP levels were determined using a cGMP assay kit (n = 5). f The relaxation response of de-endothelialized miR-155−/− (KO) aortic rings to SNP was measured by myography (n = 5). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01