FIGURE 1.
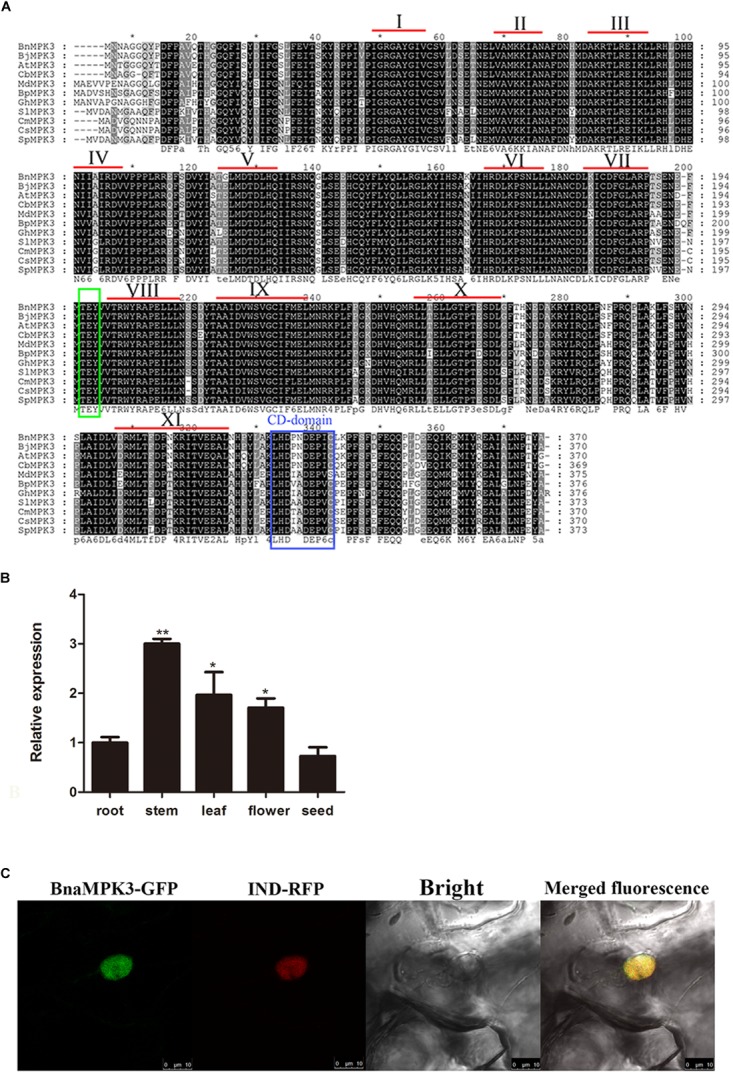
Sequence analysis of BnaMPK3. (A) Sequence alignment of BnaMPK3 and its homologs. The amino acid sequence of BnaMPK3 was aligned with those of the 10 closest matching proteins from a BLAST search. Identical amino acids are shown in black boxes, and similar amino acids are shown in gray boxes. The highly conserved domain TEY is shown in green box. The CD-domain is shown in blue box. According to Hanks and Hunter (1995), 11 subdomains (I–XI) are indicated by Roman numerals. Species abbreviations are as follows: Bn: Brassica napus; Bj: Brassica juncea; At: Arabidopsis thaliana; Cb: Chorispora bungeana; Md: Malus domestica; Bp: Betula platyphylla; Gh: Gossypium hirsutum; Sl: Solanum lycopersicum; Cm: Cucumis melo; Cs: Cucumis sativus, Sp: Solanum peruvianum. (B) Expression profiles of BnaMPK3. Relative expression levels of BnaMPK3 in different tissues were determined by real-time quantitative PCR. Values are means of three replicates. The error bars show the standard deviation. The significances of between each tissue and root are indicated (Student’s t-test, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗0.001 < P < 0.01 or ∗0.01 < P < 0.05). (C) Subcellular localization of BnaMPK3. In planta localization in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves of BnaMPK3-green fluorescent protein (GFP), IND (nuclear marker protein)-red fluorescent protein (RFP) and merged fluorescence from RFP and GFP.
