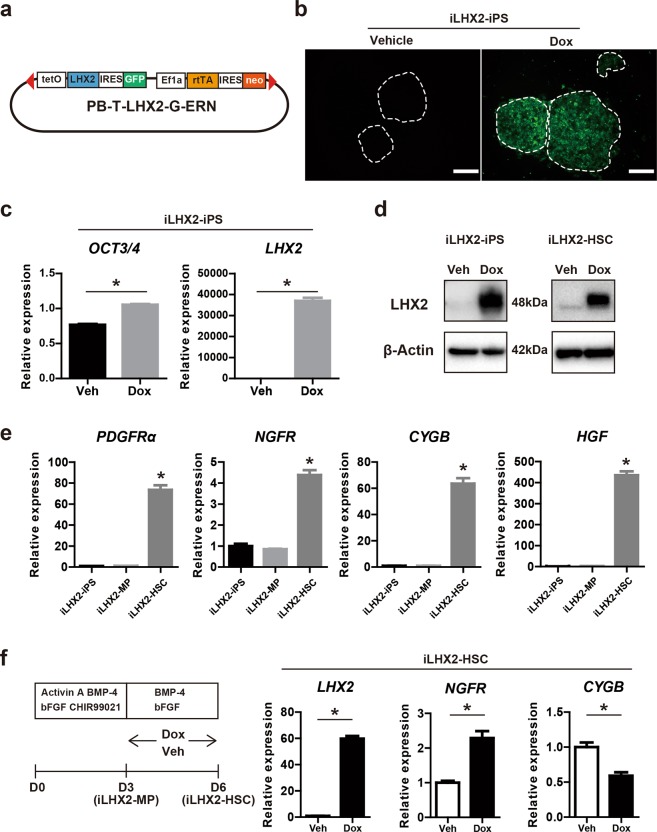
Figure 3.
Generation of iPS cell lines doxycycline-inducible overexpressing LHX2 (iLHX2) and differentiation of iLHX2 into iPS-HSCs. (a) Schema for construct of a self-contained, drug-inducible expression vector based on the PiggyBac transposon (PB-T-LHX2-G-ERN) used in this study. Tetracycline resistant operon (tetO), LHX2 gene, internal ribosomal entry site (IRES), green fluorescence protein (GFP), EF1α promoter sequences (EF1α), reverse tetracycline transactivator gene (rtTA), and neomycin-resistant gene (neo) are shown. (b) Representative view of pooled iPS cell clones containing genomic transposon integrations of LHX2 (iLHX2-iPS). Activation of LHX2 expression in response to Dox was indirectly monitored by co-incident GFP (green). Scale bars: 200 μm. (c) Expression of OCT3/4 and LHX2 in iLHX2-iPS clones cultured with vehicle (Veh) or doxycycline (Dox). The y-axis represents the ratio of expression relative to the means of iPS cells. (d) Immunoblot analysis of iLHX2-iPS clones and iPS-HSCs derived from iLHX2-iPS clones (iLHX2-HSC), which were cultured with Veh or Dox. (e) Expression of PDGFRα, NGFR, CYGB, and HGF in iLHX2-iPS clones, iPS-MP derived from iLHX2-iPS clones (iLHX2-MP), and iLHX2-HSCs, which were cultured without Dox. (f) Left panel: protocol for iLHX2-HSCs cultured with Dox at days 4–6. Expression of LHX2, NGFR, and CYGB in iLHX2-HSCs cultured with Veh or Dox. Results represent the mean ± SD of three separate experiments. *P < 0.05.