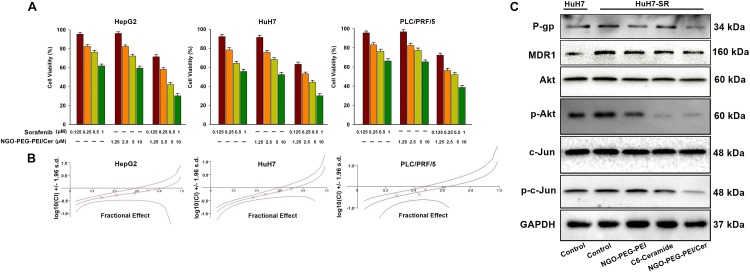
FIGURE 4.
NGO-PEG-PEI/Cer enhances sorafenib-mediated growth inhibition in HCC cells. (A) Cells were treated with NGO-PEG-PEI/Cer and/or sorafenib for 48 h, and cell viability was then determined by MTT assay. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three separate experiments. (B) The potential synergistic effect of sorafenib combined with NGO-PEG-PEI/Cer on HCC cells was assessed by Chou–Talalay Combination Index (CI) analysis using the CalcuSyn software. The middle curve line indicates the simulated combination index values, which are expressed as the log10 (CI) ± 1.96 SD, encircled by two lines of algebraic evaluation of the 95% confidence intervals. The log10 (CI) values attained at given fractional affects represent an antagonism between the treatments when >0, an additive efficiency when equal to 0 and a synergism when <0. This was quantified by CIN analysis and expressed as CIN versus fraction affected. Where calculable, 95% confidence intervals are shown. (C) The sorafenib-resistant HuH7 cell line (HuH7-SR) was used to illuminate the mechanism by which NGO-PEG-PEI/Cer may influence sorafenib-resistant HCC. NGO-C6(10 μM), C6-ceramide (10 μM), or NGO (100 μg/ml) was used to treat HuH7-SR cells. Uninfected cells served as control. Forty eight hours later, whole cell extracts were prepared and immunoblotted. GAPDH was used as a loading control.