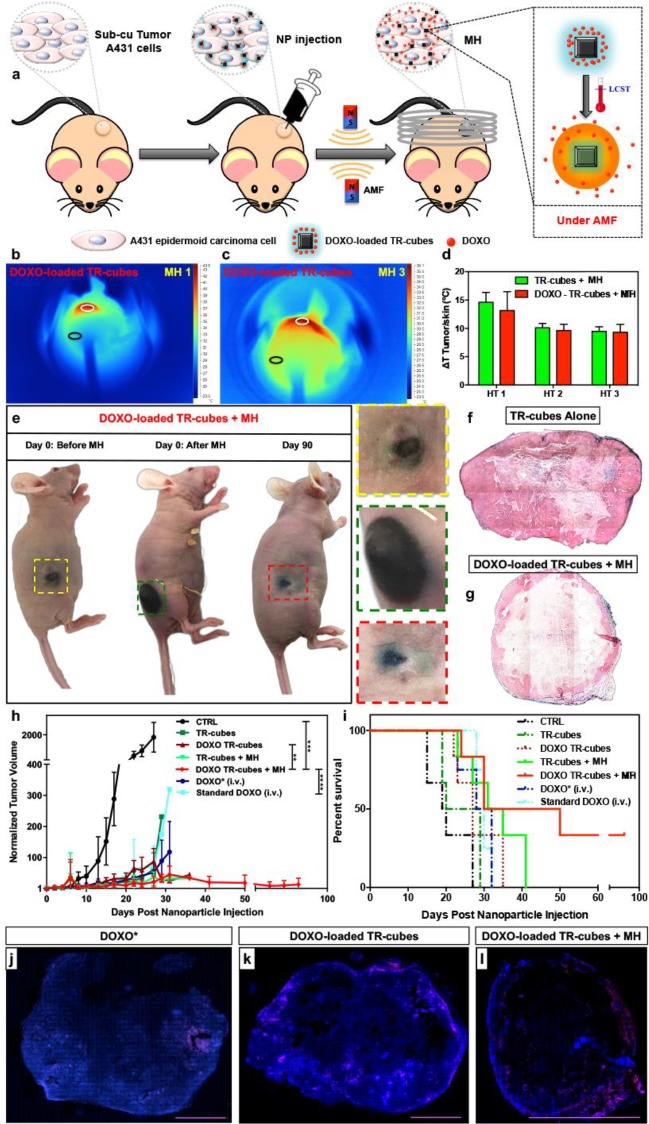
Figure 3.
TR-cubes as an effective in vivo heat mediator and controlled drug delivery system. (a) Scheme of the in vivo efficacy study. (b, c) Infrared images showing the heating of DOXO-loaded-TR-cubes at day 1 (b, MH1) and day 3 (c, MH3). (d) Plot of the temperature difference (ΔT) between TTumor (white circle) and TSkin (black circle), showing a 15 °C rise after MH1 and 10 °C after MH2 and MH3. (e) Photos of the animal after TR-cube injection (left animal), after the first MH cycles (middle), and at 90 days (right animal). Mice treated with DOXO-loaded-TR-cubes + MH showed complete tumor suppression by day 90 post-treatment (color coded inserts show enlarged images of the tumor). The photos of the three mice do not correspond to the same animal. (f, g) Histological sections of tumor treated with TR-cubes alone (f, intact stroma) or DOXO-loaded-TR-cubes + MH (g, thin stroma) stained with Prussian Blue for iron and Fast Red dye for collagen. (h, i) Tumor growth curve and Kaplan−Meier survival plot showing the difference in tumor suppression and improved survival between the DOXO-loaded-TR-cubes + MH and the other groups studied. The DOXO-loaded-TR-cubes + MH group in the tumor growth curve showed significant improvement in tumor suppression in comparison to the control group (with p = 0.0002 (***)), the standard DOXO group (p < 0.0001 (****)), and the DOXO-TR-cube group (p = 0.0035 (**)). (j−l) Confocal images of the whole tumor slice, which was sacrificed 30 days post treatment, showing the presence of viable cancer cells (DAPI blue staining) and DOXO (red signal, shown in pink due to the merge with DAPI) for DOXO* (j), DOXO-loaded TR-cubes (k), and DOXO-loaded TR-cubes + MH (l). The scale bar represents 0.5 cm.