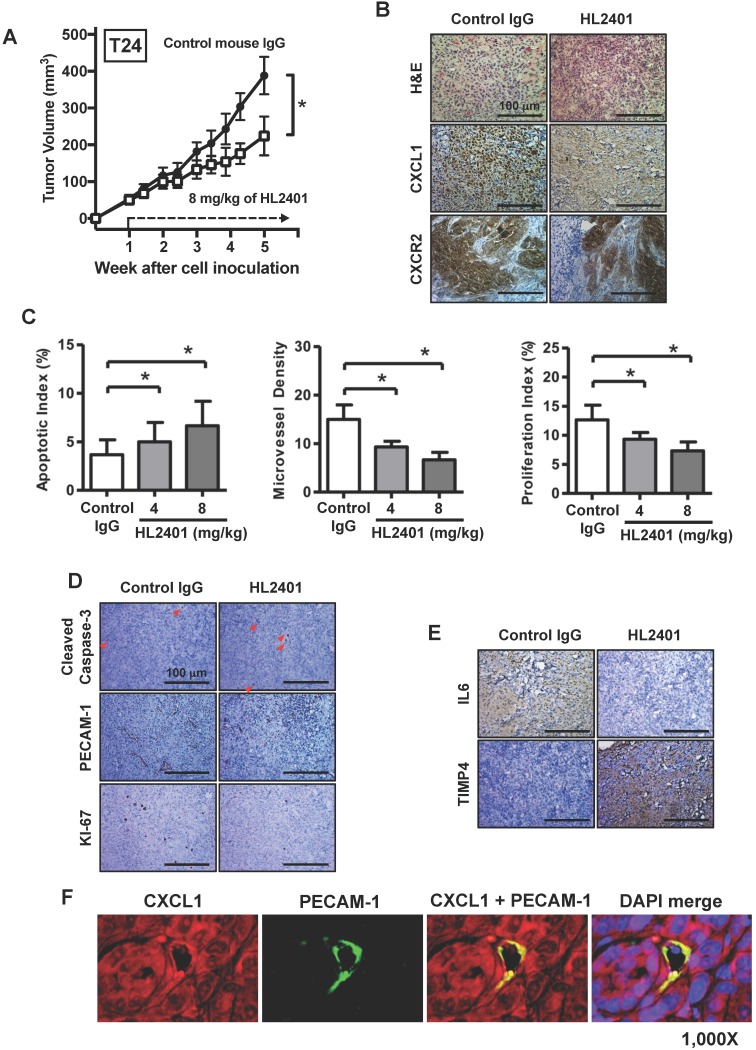
Figure 6.
Effect of targeting CXCL1 on T24 bladder xenograft tumor growth. Tumor growth was established by subcutaneous injection of parental T24 cells into athymic mice (nu/nu). HL2401 (8 mg/kg), a neutralizing monoclonal antibody to CXCL1, was injected intraperitoneally as described in Materials and Methods. Sterile PBS injection served as control. A, Tumor size, recorded over 5 weeks, was plotted as mean ± SD for three treatment groups per cell line (n=10/group). Statistical significance is represented by *, p < 0.05. Treatment with HL2401 (8 mg/kg) was associated with a reduction in tumor burden. B, H&E staining, CXCL1 and CXCR2, immunostaining of tumors are shown (original magnification 200 ×). A reduction in CXCL1 was noted in tumors treated with HL2401. C, Apoptotic index (AI) was quantified based on caspase-3 immunostaining. MVD was quantified based on PECAM-1 immunostaining. Proliferative index (PI) was quantified based on Ki-67 immunostaining. Data are presented as mean ± SD, *, p < 0.05. D, Immunostaining of tumors corresponding to AI, MVD and PI (original magnification 200 ×). E, IL6 and TIMP4 immunostaining of tumors are shown (original magnification 200 ×). A reduction in IL6, while an increase in TIMP4 was noted in tumors treated with HL2401. F, Immunofluorescent staining of xenograft tumors. CXCL1 and PECAM-1 immunofluorescent staining of tumors treatment with HL2401 (200 μg) are shown (original magnification 1000x), demonstrating CXCL1 expression with tumor epithelia as well as in tumor vasculature.