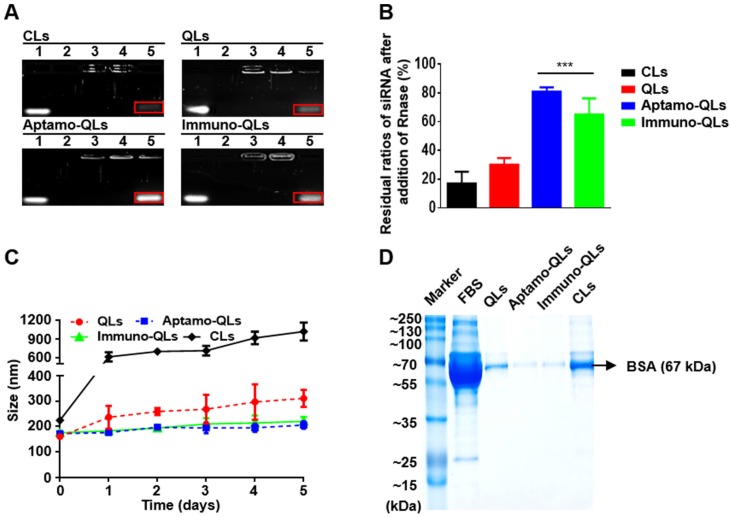
Figure 1.
siRNA protection and serum stability of aptamo-QLs and immuno-QLs. (A) Lipid nanocarriers were incubated with RNase A and siRNAs were then recovered after treatment with Triton® X-100. The recovered siRNAs were electrophoresed on agarose gel. Lane 1, free siRNA; lane 2, RNase A-treated free siRNA; lane 3, lipid nanocarriers; lane 4, RNase A-treated lipid nanocarriers; and lane 5, RNase A/Triton X®-100-treated lipid nanocarriers. The bands in red squares indicate the remaining intact siRNAs. (B) Residual ratios of intact siRNA were estimated by comparison with the amount of siRNA added. Each error bar represents the mean ± S.D. for 3 separate experiments. ***p < 0.001 vs. CLs. (C) Lipid nanocarriers were incubated in the presence of 50% FBS at 37°C and their changes in size were examined by dynamic light scattering. Each error bar represents the mean ± S.D. for 3 separate experiments. (D) Lipid nanocarriers were incubated in the presence of 50% FBS for 5 days, washed, and electrophoresed on SDS-PAGE. Lane 1, markers; lane 2, FBS; lane 3, QLs; lane 4, aptamo-QLs; lane 5, immuno-QLs; lane 6, CLs.