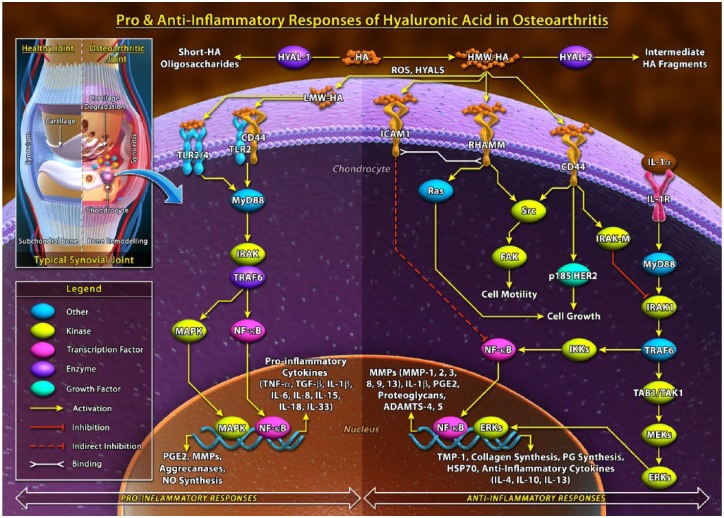
Figure 1.
Summary of the pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses of hyaluronic acid.
CD44 = cluster determinant 44; ECM = extracellular matrix; ERKs = extracellular signal-regulated kinases; FAK = focal adhesion kinase; HA = hyaluronic acid; HER2 = human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; HYAL = hyaluronidase; ICAM = intercellular adhesion molecule–1; ICM = intracellular matrix; IL = interleukin; IRAK = interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase; MAPK = mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase; MMP = matrix metalloproteinase; MyD88 = myeloid differentiation primary response 88, NF-κB = nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NO = nitric oxide; PG = proteoglycan; PGE = prostaglandin E2; TAK1 = transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-activated kinase; TAL1 = T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia protein 1; TIMP = tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases; TLR = toll like receptor; TNF = tumor necrosis factor; TRAF6 = TNF receptor associated factors.