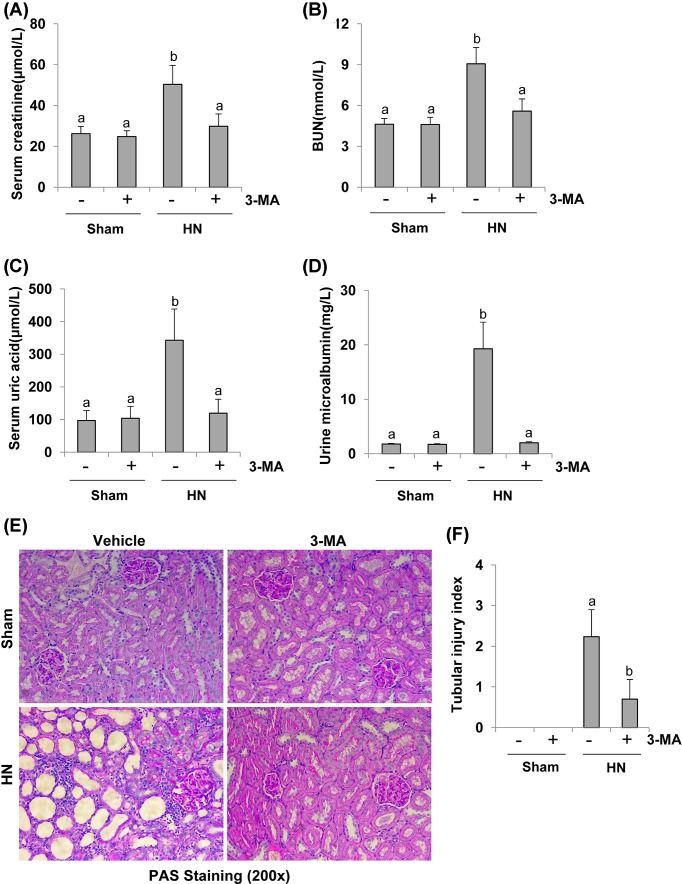
Figure 4. Administration of 3-MA reduces proteinuria, improves renal dysfunction, and attenuates renal pathological impairment in hyperuricemic rats.
Blood was collected after 3 weeks of daily feeding of the mixture of adenine and potassium oxonate with or without 3-MA administration in male Sprague–Dawley rats. Expression levels of serum creatinine (A), serum BUN (B), serum uric acid (C), and urine microalbumin (D) were examined by using automatic biochemistry assay. Photomicrographs (200×) illustrate PAS staining of the kidney tissues in control or HN rats with/without 3-MA (E). Tubular morphologic changes (epithelial necrosis, luminal necrotic debris, and tubular dilation) in 3–4 sections per kidney and 10–12 fields per section were quantitated using the following scale: normal = 0; injury < 30% = 1; 30–60% = 2; and injury > 60% = 3 (F). Data are represented as the mean ± S.E.M. (n=6). Means with different superscript letters are significantly different from one another (P<0.05).