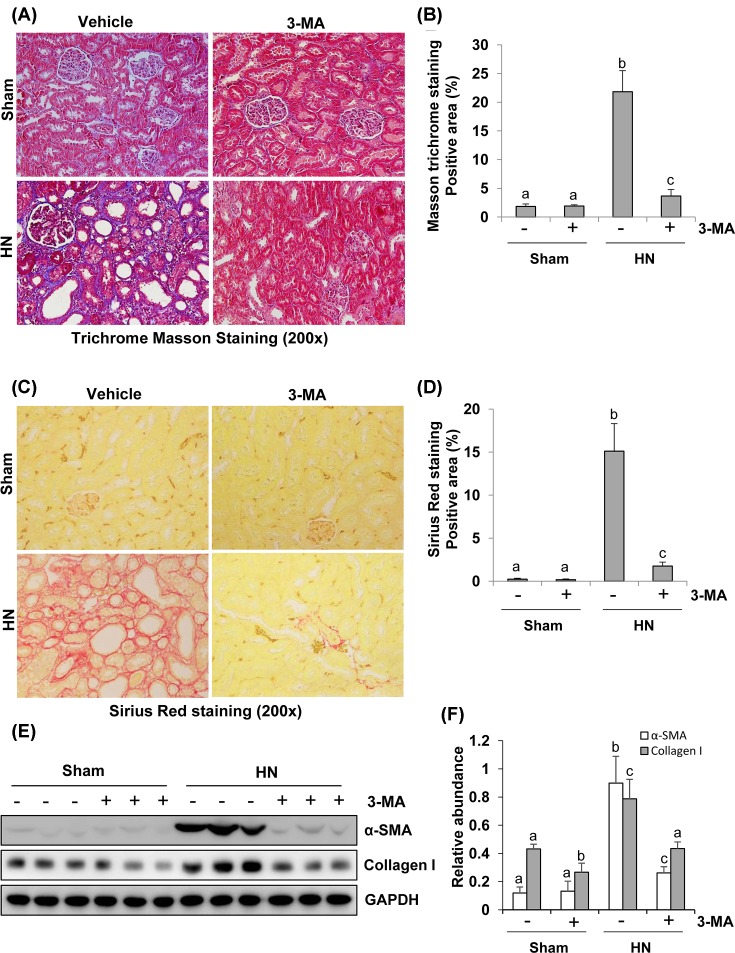
Figure 6. Administration of 3-MA attenuates development of renal fibrosis in hyperuricemic rats.
Photomicrographs (200×) illustrate Masson’s trichrome staining of kidney tissue collected after 3 weeks of daily feeding of the mixture of adenine and potassium oxonate with or without 3-MA administration (A). The Masson’s trichrome-positive tubulointerstitial areas (blue) relative to the whole area from ten random cortical fields were quantitatively measured by using ImagePro Plus software by drawing a line around the perimeter of positive staining area, and the average ratio to each microscopic field (200×) was calculated and graphed (B). Photomicrographs illustrate Sirius Red staining of kidney tissue (200×) (C). The Sirius Red-positive tubulointerstitial areas (red) relative to the whole area from ten random cortical fields were analyzed (D). The prepared tissue lysates from sham or hyperuricemic kidneys of rats treated with/without 3-MA were subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies against α-SMA, Collagen I, or GAPDH (E). Expression levels of α-SMA and collagen I were respectively quantitated by densitometry and normalized with GAPDH (F). Data are represented as the mean ± S.E.M. (n=6). Means with different superscript letters are significantly different from one another (P<0.05).