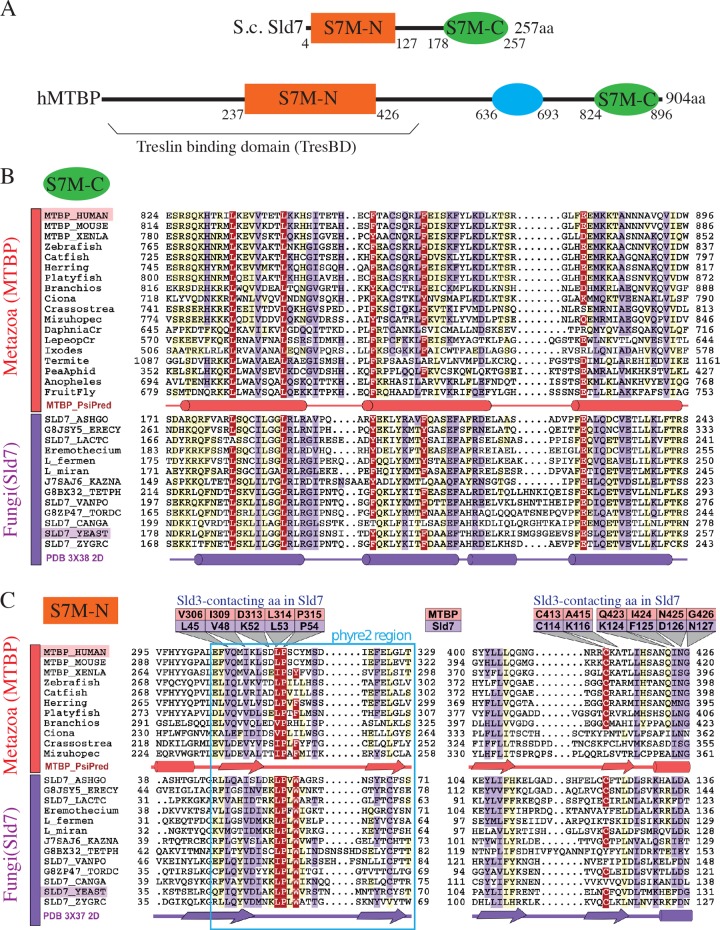
Fig 1. hMTBP and yeast Sld7 share two homologous domains, Sld7-MTBP-N and -C (S7M-N and -C).
(A) Domain architecture of hMTBP and S.c. Sld7. S7M-N, -C, conserved domains; blue oval, metazoa-specific domain. (B,C) Multiple sequence alignments of (B) S7M-C and (C) S7M-N domains. Sequences from representative metazoa (red) or fungi (purple) presented with Belvu using a colouring scheme indicating the average BLOSUM62 scores (that correlate with amino acid conservation): red (>2.5), violet (between 2.5 and 0.8), and light yellow (between 0.8 and 0.3). Predicted or known secondary structures are indicated: cylinders, α-helices; arrows, β-strands. Amino acids discussed in the main text are indicated with hMTBP or yeast Sld7 numbering (panel C). Blue box (panel C) indicates the phyre2 region. aa, amino acid; BLOSUM62, blocks substitution matrix 62; hMTBP, human MTBP; MTBP, Mdm2 binding protein; phyre2, protein homology/analogy recognition engine V 2.0; S.c., Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Sld7, synthetic lethal with Dpb11; S7M-C, Sld7-MTBP C-terminal domain; S7M-N, Sld7-MTBP N-terminal domain.