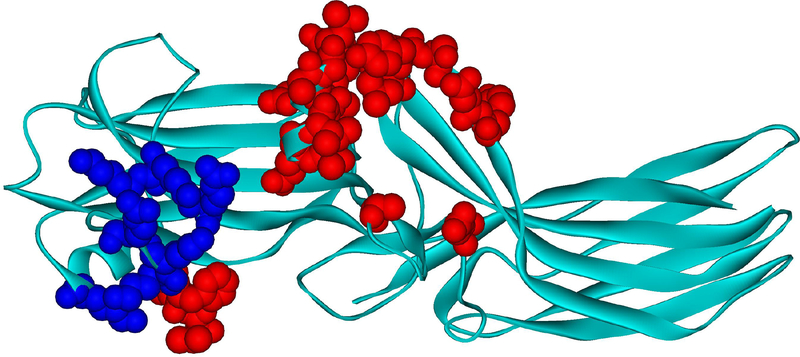
Fig. 3. Arrestin-1 residues contacting rhodopsin in co-crystal.
Mouse arrestin-1 residues that directly interact with rhodopsin are shown as CPK models (based on rhodopsin-bound mouse arrestin-1 structure from complex A, PDB ID: 4ZWJ (Kang et al., 2015)). Those that bind receptor-attached phosphates or negative charges in the rhodopsin C-terminus are colored dark blue (Zhou et al., 2017)(mouse arrestin-1 residues Lys15, Lys16, Arg19, Lys111, Lys167, Lys168, Arg172), those that interact with unphosphorylated parts of the rhodopsin molecule are colored red (Kang et al., 2015; Zhuo et al., 2014) (Val12, Ile13, Phe14, Gln70, Glu71, Ile73, Asp74, Met76, Gly77, Leu78, Arg82, Asp83, Leu84, Lys142, Leu250, Tyr251, Ser252, Asp254, Tyr255, Arg292, Thr320).