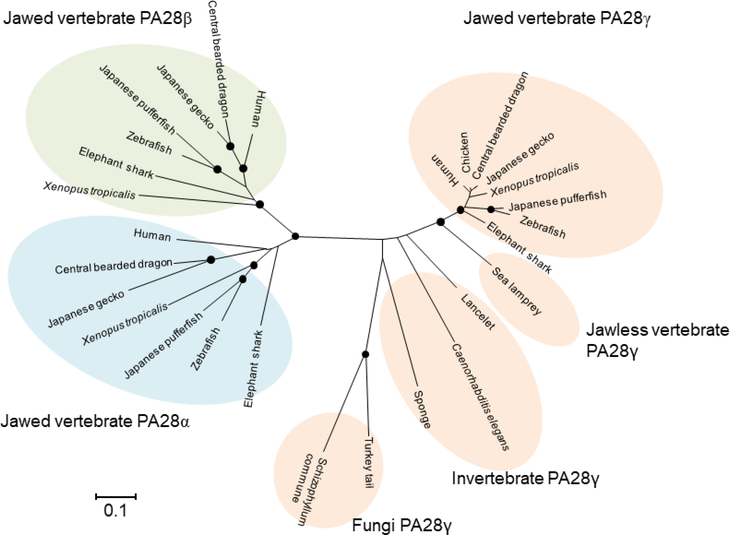
Fig. 4.
Evolution of PA28 subunits
For the construction of the phylogenetic tree, amino acid sequences of PA28α, PA28β and PA28γ subunits identified by database searches were aligned using the default Auto setting of the version 7.0 MAFFT program (Kuraku et al. 2013). The tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining algorithm implemented in the MEGA6 program package (Tamura et al. 2013). The distance matrix was obtained by calculating Poisson correction distances for all pairs of sequences. Gaps were excluded using the pairwise-deletion option. The reliability of branching patterns was assessed by bootstrap analysis (1,000 replications). Nodes supported by bootstrap values over 95% are indicated by closed circles. DDBJ/EMBL/NCBI accession numbers are as follows: human PA28α, CAG46459.1; human PA28γ, CAG46543.1; human PA28γ, CAG46545.1; chicken PA28γ, CAG31370.1; central bearded dragon PA28α, XP_020664971.1; central bearded dragon PA28β, XP_020664964.1; central bearded dragon PA28γ, XP_020651679.1; Japanese gecko PA28α, XP_015270891.1; Japanese gecko PA28β, XP_015272197.1; Japanese gecko PA28γ, XP_015282260.1; Xenopus tropicalis PA28α, AAH88020.1; Xenopus tropicalis PA28β, NP_001011494.1; Xenopus tropicalis PA28γ, NP_001096200.1; zebrafish PA28α, NP_571450.1; zebrafish PA28β, NP_571449.1; zebrafish PA28γ, AAF05816.1; Japanese pufferfish PA28α, XP_003967855.1; Japanese pufferfish PA28β, XP_003968209.1; Japanese pufferfish PA28γ, XP_003961088.1; elephant shark PA28α, AFM87012.1; elephant shark PA28β, JK930727; elephant shark PA28γ, XP_007907679.1; sea lamprey PA28γ, CO546357.1; lancelet PA28γ, XP_019630503.1; Caenorhabditis elegans PA28γ, NP_499493.1; sponge Amphimedon queenslandica PA28γ, XP_019856930.1; Turkey tail Trametes versicolor PA28γ, XP_008031792.1; and Schizophyllum commune PA28γ, XP_003038805.1.