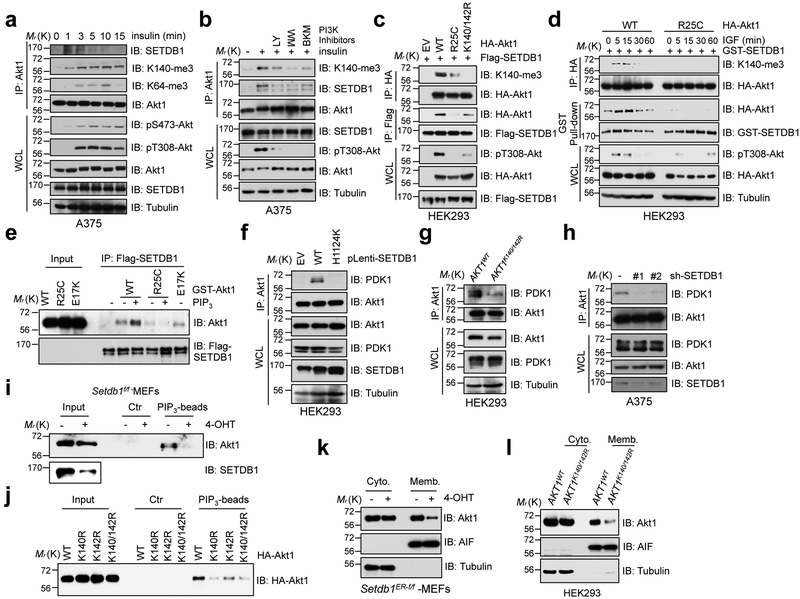
Fig. 5. SETDB1-medidated methylation of Akt synergizes with PI3K to activate Akt.
a,b, A375 cells were serum-starved for 20 hrs, then stimulated with insulin (50 nM) at different time points (a) or post-treatment of various PI3K inhibitors (b) before harvesting for IP and IB analysis. c,d, IB analysis of IP products and WCL derived from HEK293 cells transfected with indicated constructs stimulated without (c) or with IGF (100 ng/ml) (d) before harvesting. e, In vitro binding assays were performed with recombinant GST-Akt1 protein purified from mammalian cells, and flag beads bound SETDB1. The binding was performed in 4°C for 4 hrs incubated with or without PIP3 (20 μM) and subjected to IB analysis. f-h, IB analysis of Akt1-IP and WCL derived from HEK293 cells infected with indicated SETDB1 encoding constructs (f), AKT1K140/142R and its parental HEK293 cells (g) and SETDB1 depleted A375 cells (h). i,j, IB analysis of PIP3 pull-down products and WCL derived from Setdb1 conditional knockout MEFs treated with or without 4-OHT (500 nM) for 48 hrs (i) or from HEK293 cells transfected with indicated constructs (j). Where indicated, empty beads (Ctr) serve as a negative control. k,l, IB analysis of cell fractionations separated from Setdb1 conditional knockout MEFs treated with or without 4-OHT (500 nM) for 48 hrs (k) or from AKT1K140/142R-edited and parental HEK293 cells (l). All Western-blots above were performed twice, independently, with similar results. Scanned images of unprocessed blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 8.