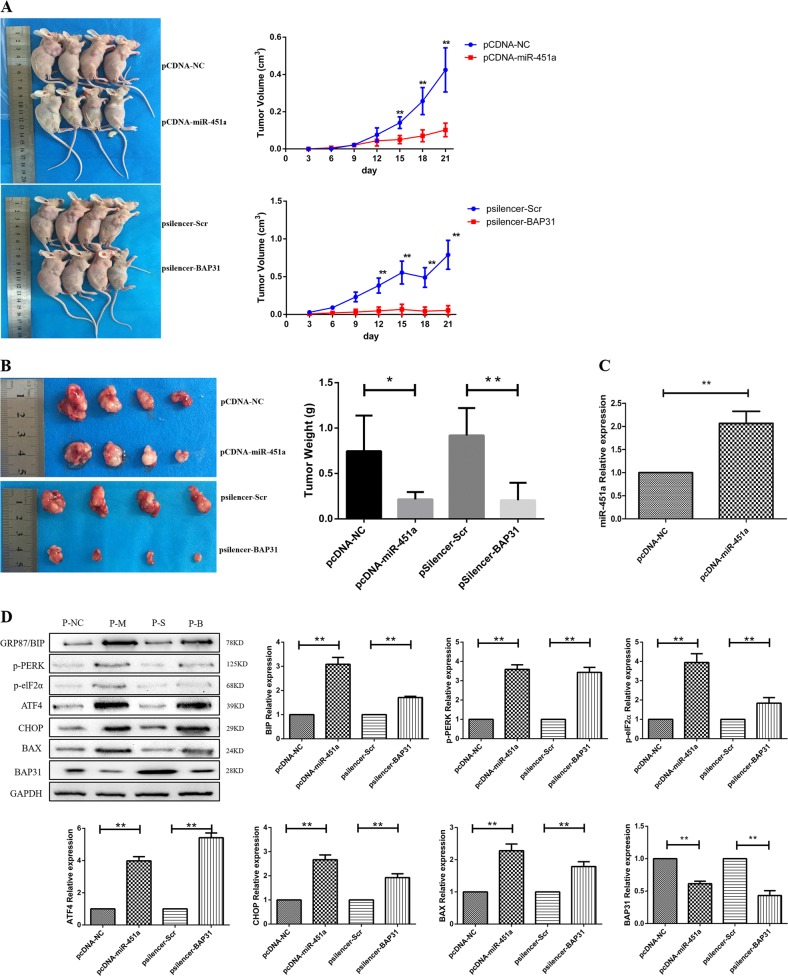
Fig. 7. Over-expressing miR-451a or silencing BAP31 inhibited tumor growth in vivo and the relative expression of miR-451a, BAP31, and ERS-associated proteins in CRC tissues of different groups of mice.
Twenty 5-week-old BALB/c-nu male mice were assigned into four groups: pcDNA-NC control group, pcDNA-miR-451a group, psilencer-Scr control group, and psilencer-BAP31 group, each group with five mice. As many as 8 × 106 cancer cells were subcutaneously injected into these mice. The weight of the mice and tumor volumes were determined every 3 days. The mice were sacrificed when administered for 21 days. The tumors were collected and weighed. a Tumor xenograft volume was smaller in nude mice treated with plasmids over-expressing miR-451a or silencing BAP31 than that in the control group. b The body weights of tumor xenografts were also lower than those of the control group (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). c The relative expression of miR-451a in xenografts administered with pcDNA-miR-451a was higher than that of the control group (**P < 0.01). d The relative expression of BAP31 was lower in pcDNA-miR-451a and psilencer-BAP31 groups than those in control groups (**P < 0.01). The expressions of ERS-associated proteins were higher in pcDNA-miR-451a and psilencer-BAP31 groups than those in control groups (**P < 0.01,*P < 0.05). CRC, colorectal cancer; ERS, endoplasmic reticulum stress