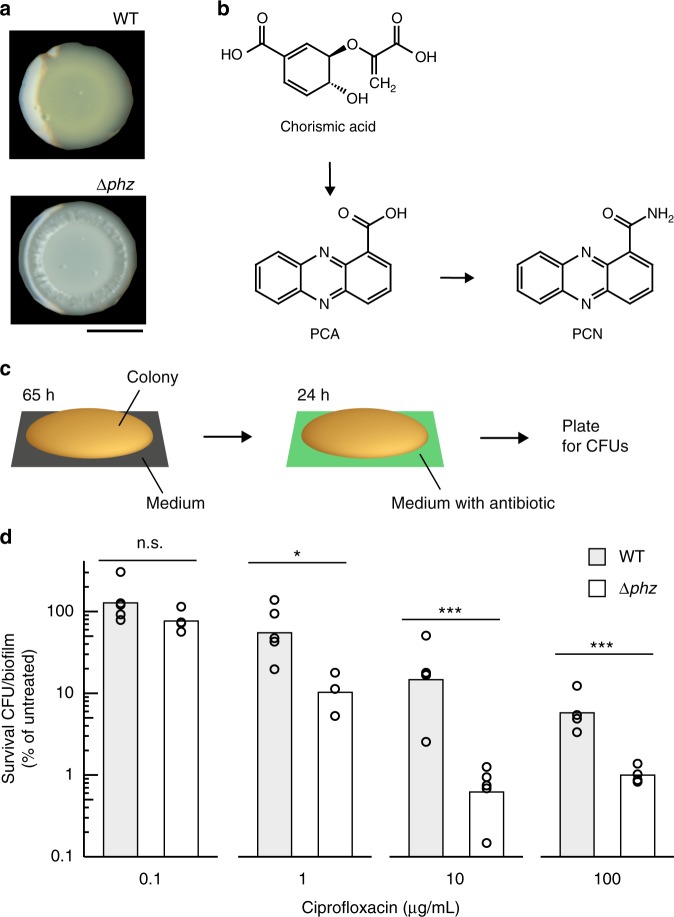
Fig. 1.
Cells from phenazine-null biofilms show increased sensitivity to ciprofloxacin. a Four-day-old colony biofilms of PA14 WT and the phenazine-null mutant (∆phz) grown on a defined medium containing 20 mM glucose. Scale bar is 5 mm. b Schematic representing the biosynthesis of phenazines produced by glucose-grown PA14 biofilms. PCA phenazine-1-carboxylic acid, PCN phenazine-1-carboxamide. c Schematic of experimental design used to quantify antibiotic tolerance in colony biofilms. d Survival of WT and ∆phz cells in biofilms exposed to ciprofloxacin at four concentrations. Each count is normalized to the CFU count reached without antibiotics (which corresponds to 100%). Data for growth without antibiotics does not show significant differences between strains (Supplementary Figure 3). Each data point is a biological replicate, bar height indicates the mean of these replicates. p values are based on two-sided unpaired t-tests (n.s., not significant; *p ≤ 0.05; ***p ≤ 0.001)