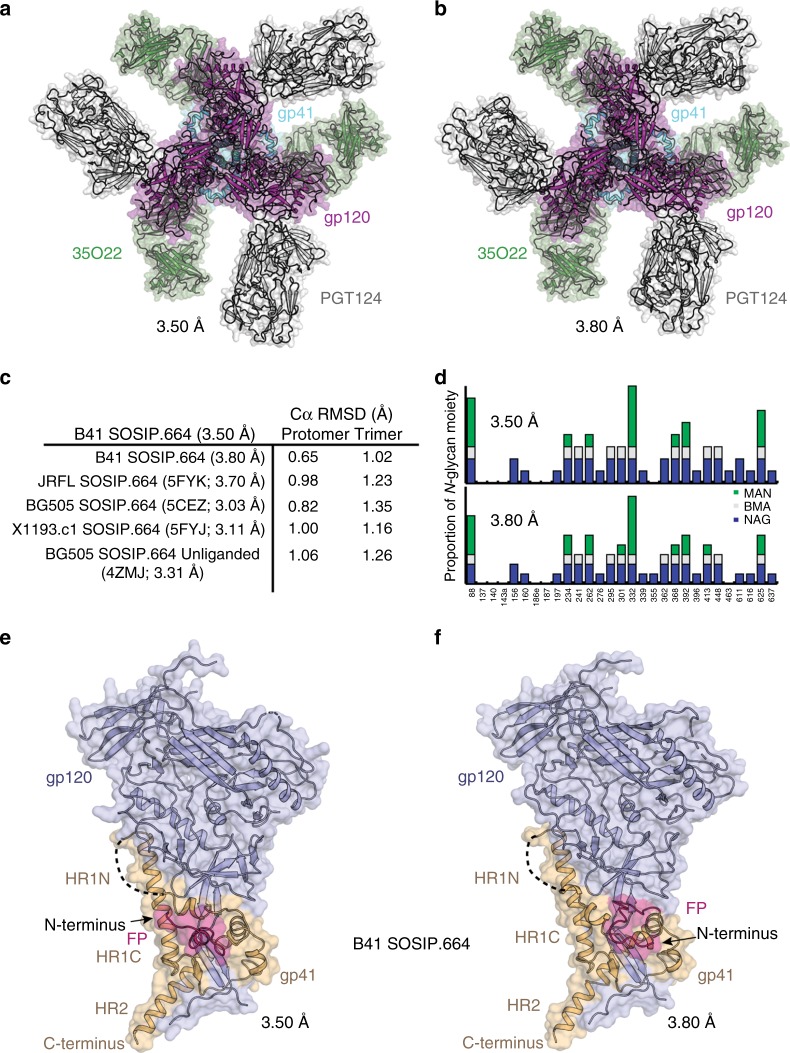
Fig. 1.
Crystal structures of closed prefusion structure of B41 SOSIP.664 Env trimer. a, b Views of the Fab complex down the trimer axis with gp120 in pink and gp41 in cyan. The cartoon representation is overlaid with a transparent molecular surface. Fabs PGT124 (dark gray) and 35O22 (green) are from the 3.50 and 3.80 Å structures in space groups P23 (a) and P63 (b), respectively. c Comparison of the protomer/trimer backbones from crystal structures of trimers of clade A (BG505 SOSIP.664, bound and unbound), B (JRFL SOSIP.664), G (X1193.c1 SOSIP.664), and the new B41 SOSIP.664 structure at 3.50 Å. d Glycosylation observed in the electron density maps in the two different B41 SOSIP.664 crystal structures. The blue, gray, and green bars along the Y-axis represent the number of N-glycan moieties of N-acetylglucosamine (NAG/GlcNAc) (maximum possible, two), β-d-mannopyranose (BMA) (maximum, one), and α-d-mannopyranose (MAN) (maximum, eight), respectively. The X-axis represents N-glycosylation sites on B41 SOSIP.664. e, f Side views of B41 SOSIP.664 protomer (gp120: light blue, gp41: light orange) in cartoon representation, overlaid with a transparent molecular surface showing two conformational states of the free N-terminus FP (pink) going away from (3.50 Å) and towards (3.80 Å) the C-terminus (i.e. proximal to the membrane)