Fig. 3.
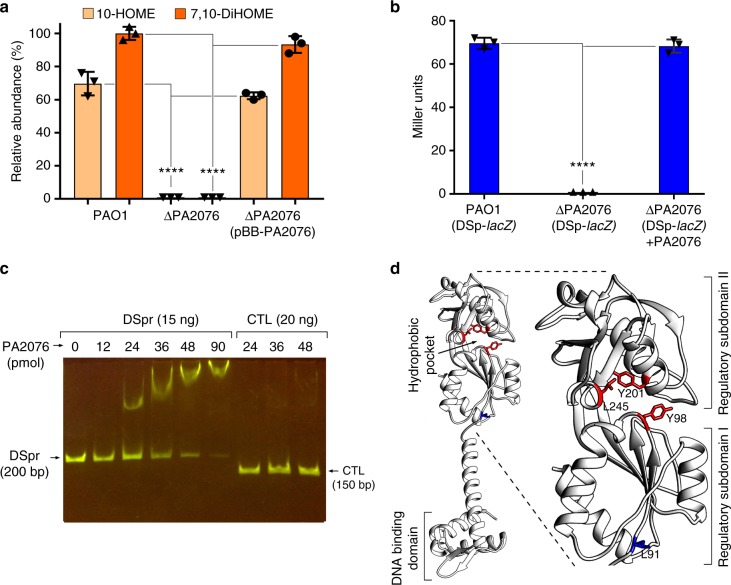
OdsR (oxylipin-dependent diol synthase regulator) is an oxylipin-dependent inducer of the diol synthase operon. a Production of oxylipins in the supernatant of PAO1, ΔPA2076 and ΔPA2076 complemented with a copy of odsR gene (ΔPA2076/pBB-odsR-His). ΔPA2076 failed to produce oxylipins. b β-Galactosidase (β-gal) expression in PAO1 (pDSp-lacZ), ΔPA2076 (pDSp-lacZ) and ΔPA2076 complemented with PA2076 [ΔPA2076 (pDSp-lacZ+pBB-odsR-His)]. ΔPA2076 (pDSp-lacZ) did not express detectable β-gal activity in the presence of oleic acid (OA; 1 mg mL−1) (t-test, P < 0.0001). c Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) gel showing specific binding of OdsR protein to the diol synthase promoter probe (DSpr, 200 bp), but not to a control unrelated DNA probe (CTL, 150 bp). d I-TASSER predicted model of OdsR three-dimensional (3D) structure. The hydrophobic pocket localized in between the two regulatory subdomains is indicated. The hydrophobic amino acids in the pocket that were replaced by hydrophilic counterparts are represented in red. These changes abolished the ability of OdsR to induce the β-gal activity of the DS-lacZ genetic fusion. The amino acid L91 (in blue) outside of the pocket had no effect on OdsR function. Data from a, b are the means and s.d. of three independent experiments. ****Significantly different, unpaired two-tailed t-test, P < 0.0001