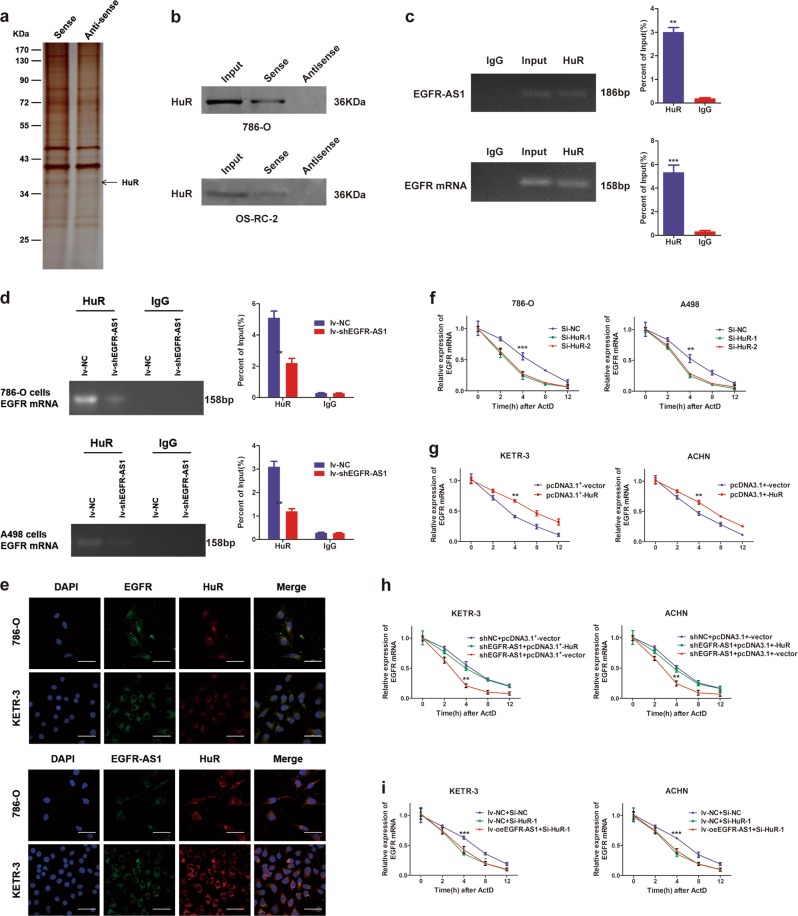
Fig. 5. EGFR-AS1 promotes the maintenance of EGFR mRNA stability by binding to HuR.
a Silver staining SDS-PAGE gel of electrophoretically separated proteins immunoprecipitated with EGFR-AS1 and its antisense RNA in 786-O cells. b RNA pull-down assay was performed in 786-O and A498 cells using biotinylated EGFR-AS1 or antisense RNA probe transcribed in vitro and detected by western blots. c Upper: RIP assays were performed in 786-O cells using HuR antibody to detect EGFR-AS1 RNA enrichment in immunoprecipitated complexes. IgG is the negative control. Lower: RIP assays were performed in 786-O cells using HuR antibody to detect EGFR RNA enrichment in immunoprecipitated complexes. d RIP assay of the enrichment of EGFR mRNA with HuR between the EGFR-AS1 knockdown and NC group in RCC cells. IgG was used as an internal control. e Upper: RNA FISH analysis of EGFR mRNA (green) and immunofluorescence detection of HuR (red) in RCC cells. The rightmost graph shows colocalization between the green signal (EGFR) and the red signal (HuR). Pearson’s R = 0.583. Scale bar = 50 μm. Lower: RNA FISH analysis of EGFR-AS1 (green) and immunofluorescence detection of HuR (red) in RCC cells. Pearson’s R = 0.416. f The rate of degradation of the EGFR mRNA between the HuR knockdown and control group using RNA stability assays in RCC cells. g The rate of degradation of the EGFR mRNA between the HuR overexpressing and control group using RNA stability assays in RCC cells. h The rate of degradation of the EGFR mRNA in the EGFR-AS1 knockdown and control cells transfected with pcDNA3.1+-HuR over 12 h in KETR-3 and ACHN cells. i The rate of degradation of the EGFR mRNA in the EGFR-AS1 overexpressing and control cells transfected with HuR siRNA over 12 h