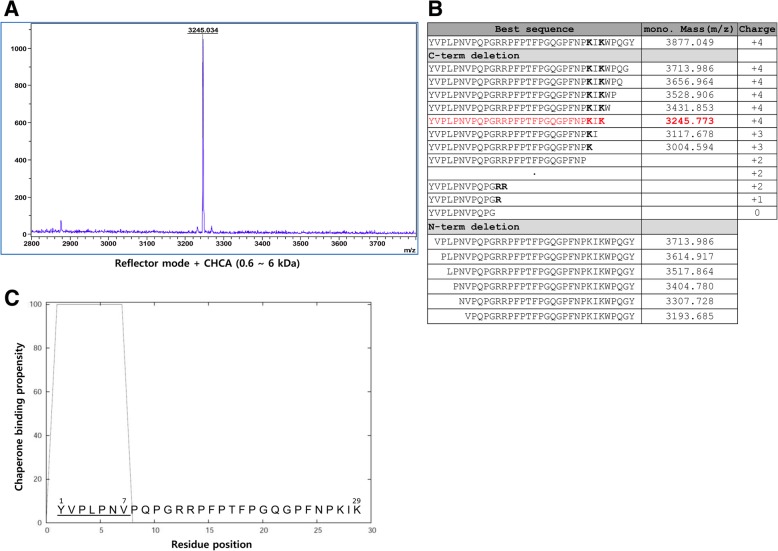
Fig. 3.
MS analysis of the cleaved-off abaecin using MALDI-TOF and investigation of binding sequence of 29-aa-long abaecin to DanK. a MS spectra obtained from reflector mode. The reflector mode was performed using α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (CHCA) matrix for the lower range of mass from 0.6 to 6 kDa to analyze the target peak at high resolution. b Table of masses and overall charge for a series of deleted peptide sequences from abaecin. Masses were analyzed for each deleted peptide sequence from either N- or C-termini in order to find the best peptide sequence matchable to the detected mass (m/z), 3245.034. Net charges at pH 7 were calculated by Peptide Property Calculator (https://www.biosyn.com/peptidepropertycalculatorlanding.aspx).The amino acids which affect the overall charge of abaecin were represented as bold fonts, such as K for Lys and R for Arg. c Sequence analysis for the binding affinity of the 29-aa-long abaecin to DnaK. The amino acid sequence of the 29-aa-long abaecin is represented, and the putative binding sequence to DnaK is underlined and numbered