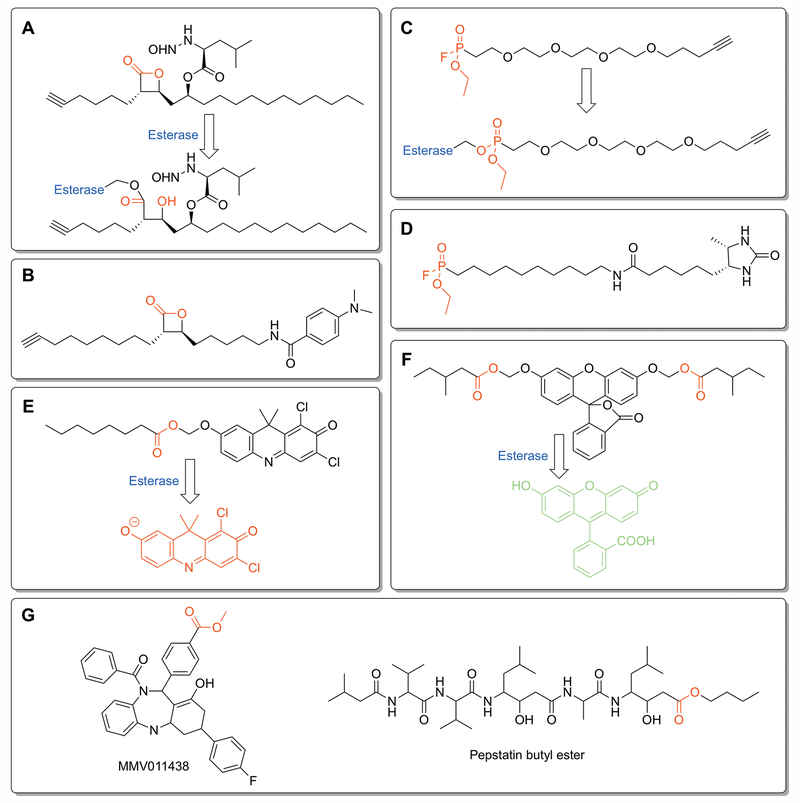
Figure 2:
Profiling bacterial esterases. A – D) Activity based protein profiling (ABPP) ligands used to characterize proteome-wide esterase activity in Mycobacteria and to identify esterase activity present under disease relevant growth conditions.[Lehmann et al. 2018; Ortega et al. 2016; Ravindran et al. 2014; Tallman et al. 2016b] Each ligand contains an electrophilic moiety (labeled in red) for covalent labeling of esterases and an alkyne for isolation and identification of labeled esterases by click chemistry. A) Tetrahydrolipstatin (THL)-alkyne.[Ravindran et al. 2014] B) Modified version of THL-alkyne (EZ120) designed to mimic mycolic acids on the Mtb mycomembrane.[Lehmann et al. 2018] C) Fluorophosphonate-PEG-alkyne.[Ortega et al. 2016] D) Desthiobiotin-fluorophosphonate.[Tallman et al. 2016b] E and F) Complementary fluorogenic ester substrates used to measure dynamic esterase activity under disease-related growth conditions.[Bassett et al. 2018; Tallman and Beatty 2015; Tallman et al. 2016a; Tallman et al. 2016b] Cleavage of ester moieties (labeled red) by a bacterial esterase transitions the fluorophore from a stable non-fluorescent form into a highly fluorescent state. Changing the ester moieties and screening the resulting fluorogenic libraries have identified ester moieties with specificity to pathogenic Mycobacteria species (E)[Tallman et al. 2016a; Tallman et al. 2016b] and to dormant growth conditions (F).[Bassett et al. 2018] E) DDAO (7-hydroxy-9H-1,3-dichloro-9,9-dimethylacridin-2-one)-acyloxymethyl ether probe.[Tallman et al. 2016a; Tallman et al. 2016b] The eight-carbon acyloxymethyl ether probe was the most selective for pathogenic Mycobacteria esterases. F) Fluorescein acyloxymethyl ether esterase probe.[Bassett et al. 2018] A variety of hydrophobic and long-chain esters, including a fluorescein bis((4-methyl)valeryloxymethyl ether) derivative, were selectively activated under nutrient starvation growth conditions. G) Two anti-malarial prodrugs selectively activated by PfPARE.[Istvan et al. 2017] The ester prodrug moiety that increases cell permeability and is selectively removed by PfPare within P. falciparum is shown in red.