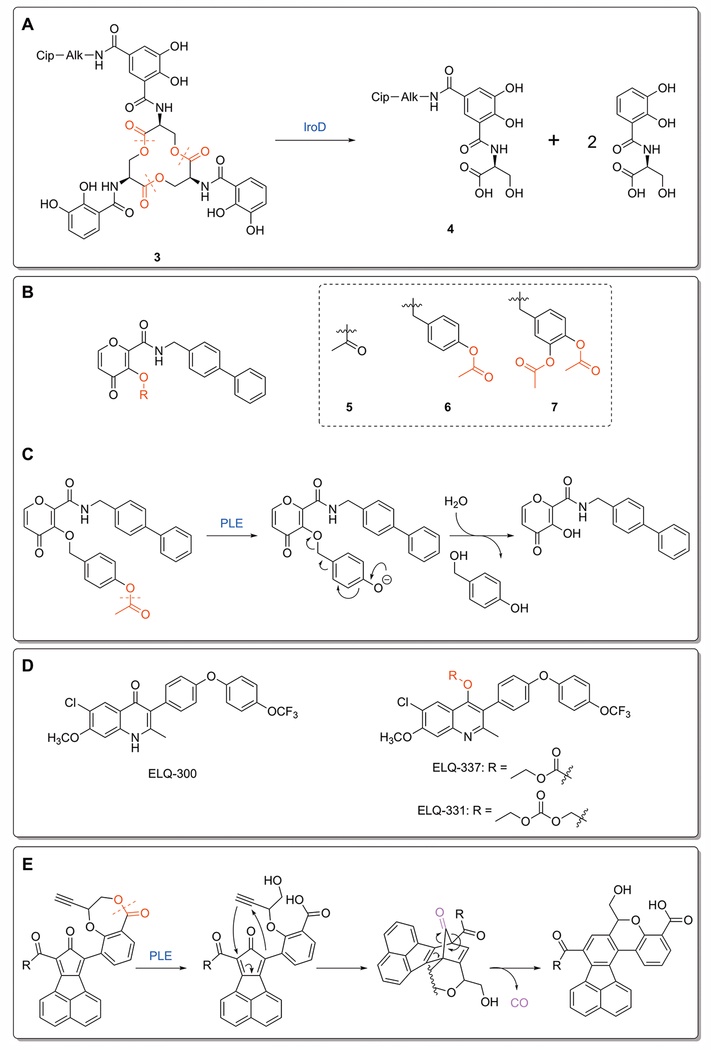
Figure 4:
Novel ester prodrugs and mechanisms. A) Decomposition of the ciprofloxacin-enterobactin conjugate 3. IroD-catalyzed hydrolysis breaks apart the siderophore, leaving behind the monocatecholate product 4.[Neumann et al. 2018] B) Ester prodrugs of the metalloproteinase proinhibitor PY-2: methyl ester 7, benzyl ether linked 8, and catechol linked 9. C) Mechanism of ester-responsive trigger for 8. Hydrolysis of the protecting methyl ester leads to decomposition of the benzyl ether, yielding the parent inhibitor.[Perez et al. 2013] D) ELQ-300 and its carbonate and alkoxycarbonate esters. The ester functionality disrupts the planar compound and decreases crystallinity, which enhances oral absorption.[Frueh et al. 2017] E) Release mechanism for metal-free CO prodrugs. Esterase activation opens the 7-membered lactone ring, freeing the alkyne functionality to undergo Diels-Alder cycloaddition with the cyclopentadienone core. The intermediate rearranges to release CO and the final cyclization product.[Ji et al. 2017]