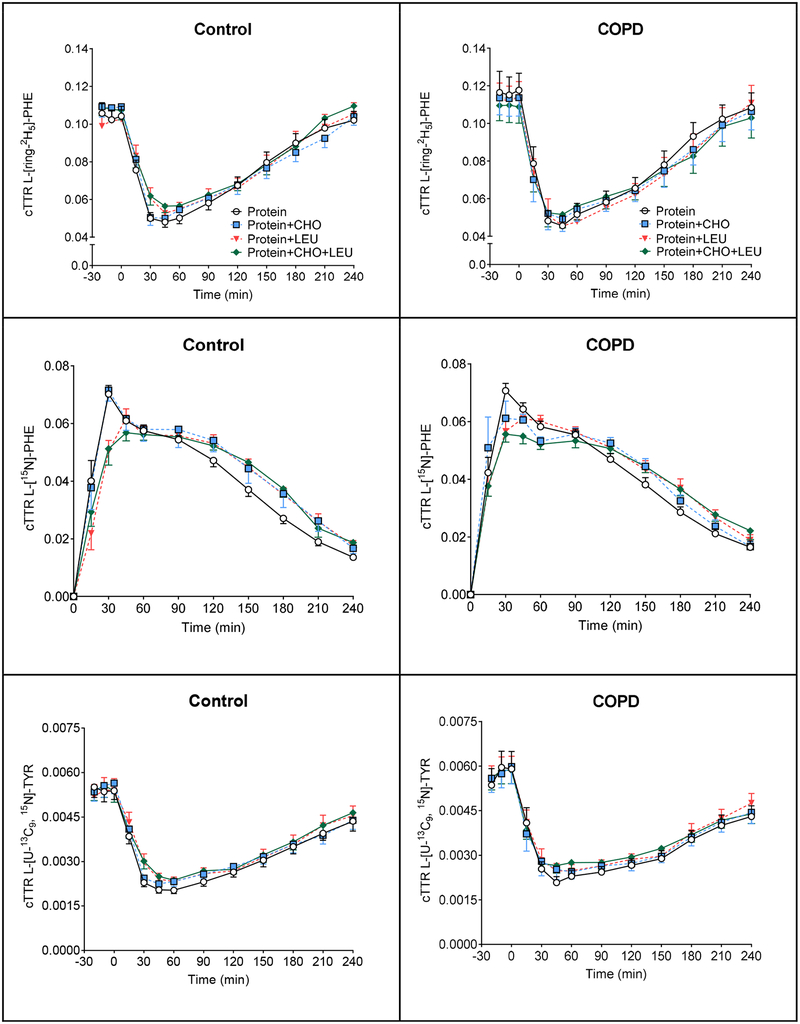
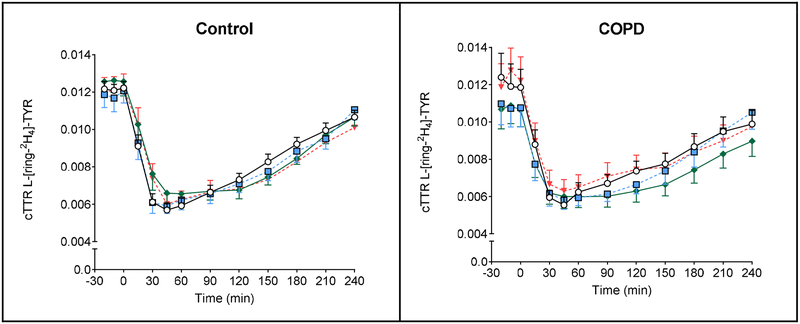
Figure 4.
Mean (± SE) plasma cTTR in healthy controls (n=11) for L-[ring-2H5]-PHE (A1), L-[15N]-PHE (B1), L-[U-13C9, 15N]-TYR (C1), and L-[ring-2H4]-TYR (D1), before and after intake of 4 different protein drinks. Protein drinks were ingested orally (at time = 0 min) and consisted of 0.6 g/kg ffm hydrolyzed casein protein with, a) no add-ons (protein), b) 0.3 g/kg ffm CHO (protein+CHO), c) 0.095 g/kg ffm leucine (protein+LEU), d) both add-ons (protein+CHO+LEU). Two-factor repeated measures analysis of variance showed a significant time effect for L-[ring-2H5]-PHE, L-[15N]-PHE, L-[U-13C9, 15N]-TYR, L-[ring-2H4]-TYR (P<0.0001) and time-by-protein drink interaction for L-[ring-2H5]-PHE, L-[15N]-PHE, L-[ring-2H4]-TYR (P<0.0001), L-[U −13C9, 15N]-TYR (P=0.07). No protein drink effects were observed for any of the measures. Mean (± SE) plasma cTTR in COPD patients (n=10) for L-[ring-2H5]-PHE (A2), L-[15N]-PHE (B2), L-[U-13C9, 15N]-TYR (C2), and L-[ring-2H4]-TYR (D2), before and after intake of 4 different protein drinks. Protein drinks were ingested orally (at time = 0 min) and consisted of 0.6 g/kg ffm hydrolyzed casein protein with, a) no add-ons (protein), b) 0.3 g/kg ffm CHO (protein+CHO), c) 0.095 g/kg ffm leucine (protein+LEU), d) both add-ons (protein+CHO+LEU). Two-factor repeated measures analysis of variance showed a significant time effect for L-[ring-2H5]-PHE, L-[15N]-PHE, L-[U-13C9, 15N]-TYR, L-[ring-2H4]-TYR (P<0.0001) and time-by-protein drink interaction for L-[15N]-PHE (P<0.0001). No protein drink effects were observed for any of the measures. CHO: carbohydrates. COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. cTTR: stable isotope tracer/tracee ratio corrected for natural abundance. ffm: fat-free mass. LEU: leucine. PHE: phenylalanine. TYR: tyrosine