Figure 3. 17βHSD2 inhibits tumor proliferation.
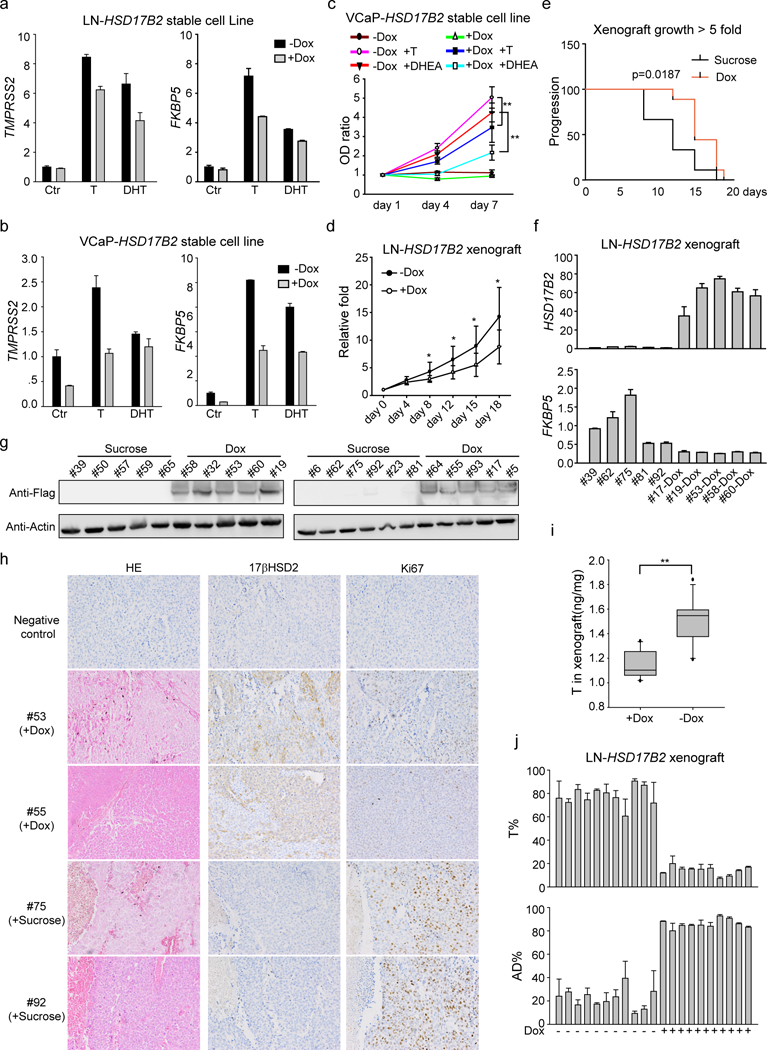
(a) and (b) Overexpression of HSD17B2 in LNCaP (a) and VCaP (b) inhibited androgen induced AR target genes expression. (c) 17βHSD2 inhibited T and DHEA induced cell proliferation. Dox (1 μg/ml) was used to induce HSD17B2 expression in VCaP. **, p<0.01. (d) and (e) HSD17B2 inhibited xenograft growth. Dox (2 mg/ml) was used to induce HSD17B2 expression. Growth curve (d) and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis (e, time for tumors reaching 5-fold size) were used to show the results of tumor growth. *, p <0.05. (f) and (g) HSD17B2 expression in xenograft. Both mRNA (f) and protein (g) level were detected in sucrose or dox treated xenograft. Fresh xenograft tumors were collected for immediate mRNA or protein detection. (h) Immunohistochemistry staining of xenograft. Ki67 was used as a proliferation marker. (i) Concentration of T in xenograft. **, p<0.01. (j) T metabolism in xenograft. Fresh xenograft was collected and treated with dox (xenografts from dox-treated group) or not (xenografts from sucrose-treated group). [3H]-T was used to treat xenograft tissues for metabolism assay.
