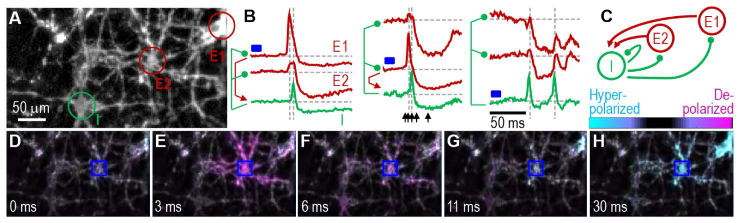
Fig. 3.
Synaptic microcircuit. Neurons were collected from an E18 rat hippocampus and cultured for 14 days. (A) QuasAr fluorescence image of excitatory cells E1 and E2 connected in a microcircuit with inhibitory cell I. (B) The digital micromirror device (DMD) is used to stimulate single cell individually, indicated by the blue rectangle, while recording from the other 2. The left of each panel shows inferred connectivity for excitatory (red) and inhibitory (green) synaptic coupling. (C) A diagram of microcircuit connectivity determined from the functional recordings in B. (D) – (H) Frames from the video where E2 is stimulated (blue square), at times indicated by black arrows in B. (D) Before cell E2 fires. (E) The stimulated cell E2 fires, which triggers (F) cell I to fire. (G) & (H) Cell I induces inhibitory post synaptic potentials in cells E1 and E2.