Figure 2.
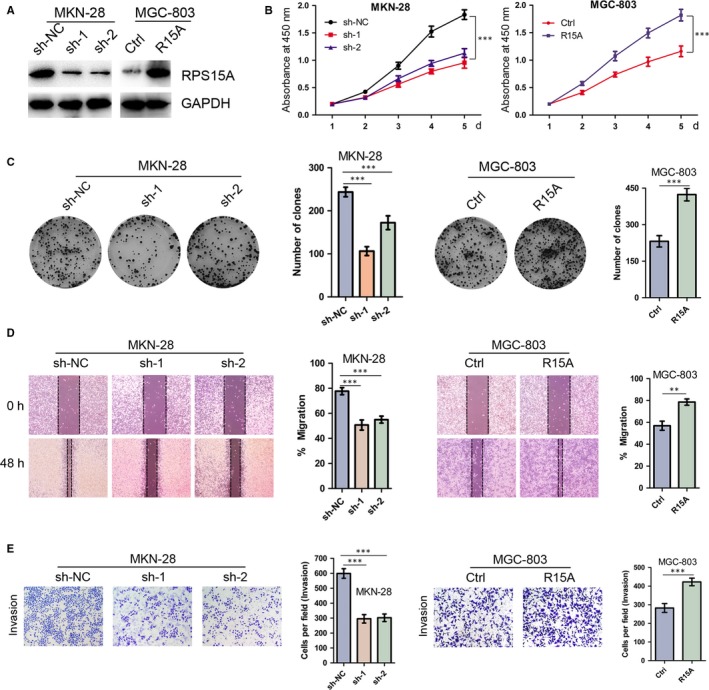
RPS15A promotes GC cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro. A, The RPS15A knockdown and overexpression effects were confirmed by Western blotting. GAPDH was used as an internal control. B, Depletion of RPS15A inhibited GC cell proliferation, whereas ectopic expression of RPS15A stimulated GC cell proliferation as determined by CCK‐8 assay. ***P < 0.001 by Student's t test. C, The effect of RPS15A on GC cell line colony formation. ***P < 0.001 by Student's t test. D, Indicated cells were subjected to scratch wound‐healing assay. The wound space was photographed at 0, and 48 h. The wound healing was measured with the following formula: 48‐h migration % = (0‐h width – 48‐h width of wound)/(0‐h width of wound). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 by Student's t test. E, The transwell invasion assays showed that depletion of RPS15A obviously inhibited the invasion of MKN‐28 cells. Conversely, the ectopic expression of RPS15A promoted the invasion of MGC‐803 cells. The data are presented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. ***P < 0.001 by Student's t test
