Figure 4.
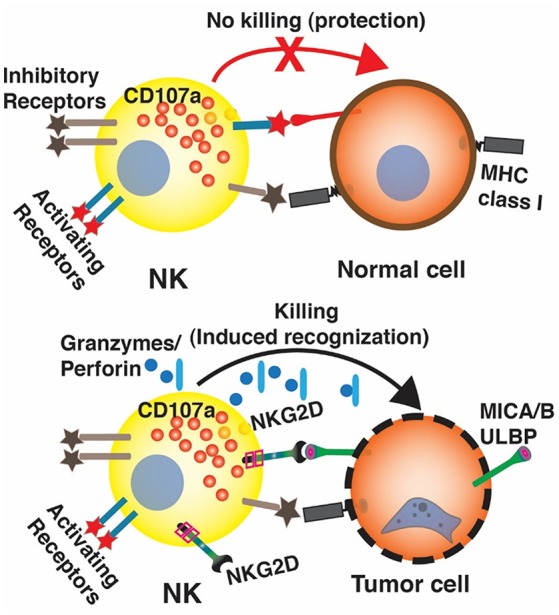
The interaction between NKG2D on NK cells and NKG2D ligands on tumor cells. In normal cells, NKG2D ligands express is very low. The functions of NK cells are balanced by the signals from the inhibitory and activating receptors. In humans, when normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. NKG2D ligands such as MICA/B and ULBP proteins, are often overexpressed. The engagement of NKG2D and NKG2D ligands overcomes inhibitory signals on NK cells, activates NK cells to release cytotoxic molecules such as perforin and granzyme, and trigger apoptosis of tumor cells.
