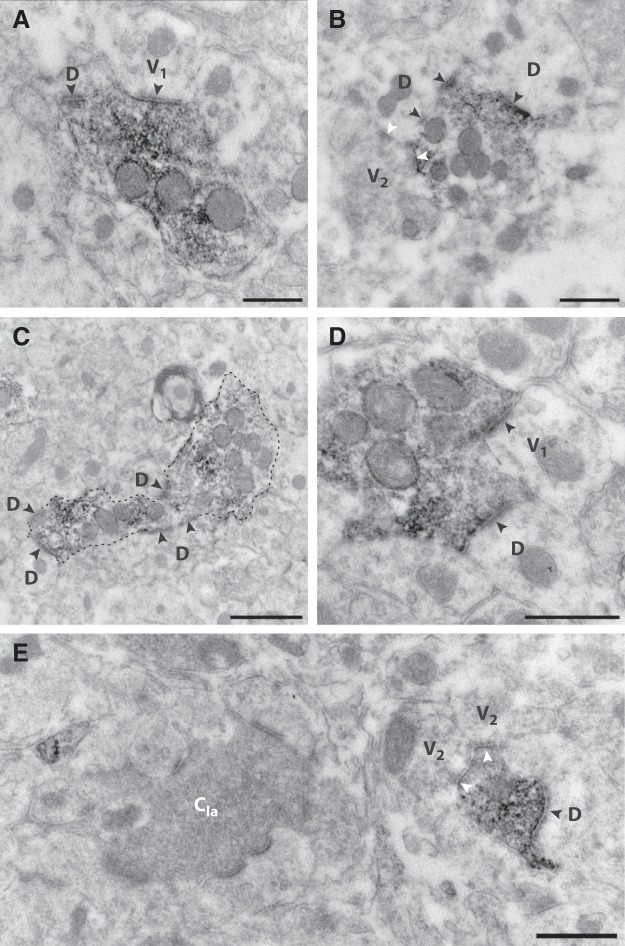
Figure 6.
Ultrastructural identification of C-LTMR terminals in the rat. A–E, Examples of terminals showing preembedding immunoperoxidase labeling for VGLUT3 in lamina IIi. Each terminal shows characteristics of central terminals of Type II glomeruli, including a generally round outline, light axoplasm, loosely packed clear small-diameter synaptic vesicles and several mitochondria. The terminals form multiple asymmetric synapses with postsynaptic dendrites, some of which contain vesicles that likely store GABA and thus originate from inhibitory neurons. Peripheral axons form inhibitory symmetric synapses onto either the central terminal (E) or a dendrite, or both (B). In E, a Type Ia glomeruli is adjacent to a VGLUT3+ terminal. Note that the central terminal of the Type I glomeruli (CIa), presumably originating from a non-peptidergic IB4 binding C fiber, exhibits no peroxidase labeling. D, postsynaptic dendrite lacking vesicles; V1, postsynaptic vesicle-containing dendrite; V2, vesicle-containing presynaptic axon. Black and white arrowheads indicate the postsynaptic aspect of asymmetric and symmetric synapses, respectively. Dashed line in C outlines the terminal for clarity. Scale bars, 500 nm (A, B, D, E) and 1 µm (C).