Figure 1.
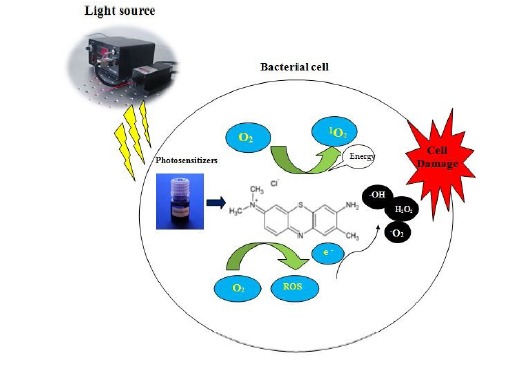
The Mchanism of Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy. Photosensitizers can be preferentially uptaken by bacteria, accumulating inside the bacteria and in the cytoplasm membranes, or in the proximity. The photosensitizer in its ground singlet state is exposed to light of a appropriate wavelength and attract a photon. Then, the photosensitizer transferral energy from light to molecular oxygen to produce singlet oxygen and free radicals that are cytotoxic to cells.
