Figure 1.
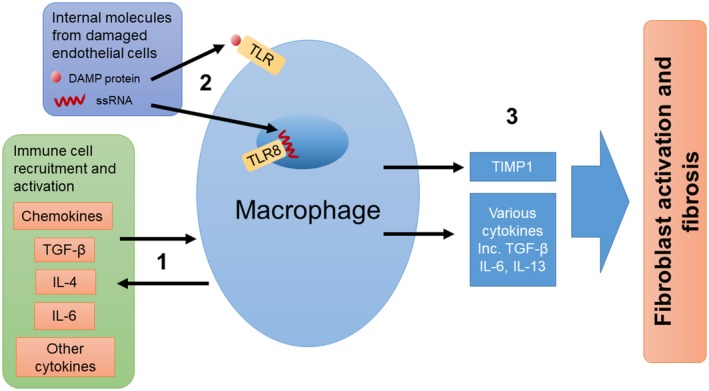
Potential roles for macrophages in the immunopathogenesis of SSc. (1) Macrophages can both be activated by and release cytokines. Cytokines and chemokines released by macrophages may recruit and activate other immune cells to further promote an inflammatory environment. (2) Internal molecules released from damaged endothelial cells can activate macrophages by Toll‐like receptors (TLRs). (3) Activation of macrophages leads to the secretion of profibrotic molecules and the activation of fibroblasts resulting in fibrosis.
