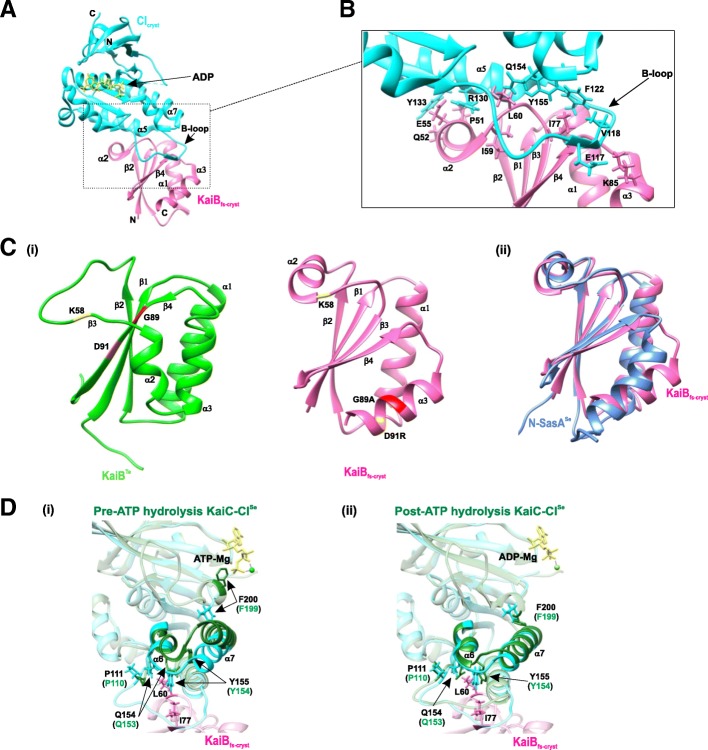
Fig. 5.
Rare active fold-switched form of KaiB (fsKaiB) binds to the post-hydrolysis state of KaiC CI domain. a A 1.8-Å resolution structure of the KaiBfs-cryst–CIcryst complex (PDB 5JWO; from T. elongates). The ribbon diagram shows KaiBfs-cryst in pink, CIcryst in cyan, and bound ADP in yellow. Enclosed dotted box depicts the binding interface between KaiBfs-cryst and CIcryst. b Enlarged view of the KaiBfs-cryst–CIcryst complex binding interface depicting the interacting residues. c Structural comparison of KaiB ground state (gs) and fsKaiB: (i) KaiBTe (gsKaiB; PDB 2QKE, subunit A) in green, KaiBfs-cryst in pink; (ii) superposition of KaiBfs-cryst in pink with N-SasASe (PDB 1T4Y; Se: S. elongatus) in cornflower blue. Residues K58, G89, and D91 are highlighted in yellow, red, and orange, respectively. d Comparison of the ATP binding site of the KaiBfs-cryst–CIcryst complex with ATP binding site of KaiC CI structures (from S. elongates) in the pre- and post-hydrolysis states: superposition of ADP-bound CIcryst (cyan) with the CISe structure (green) in the (i) pre-ATP hydrolysis state (PDB 4TLC, subunit C) and (ii) post-ATP hydrolysis state (PDB 4TLA, subunit E)