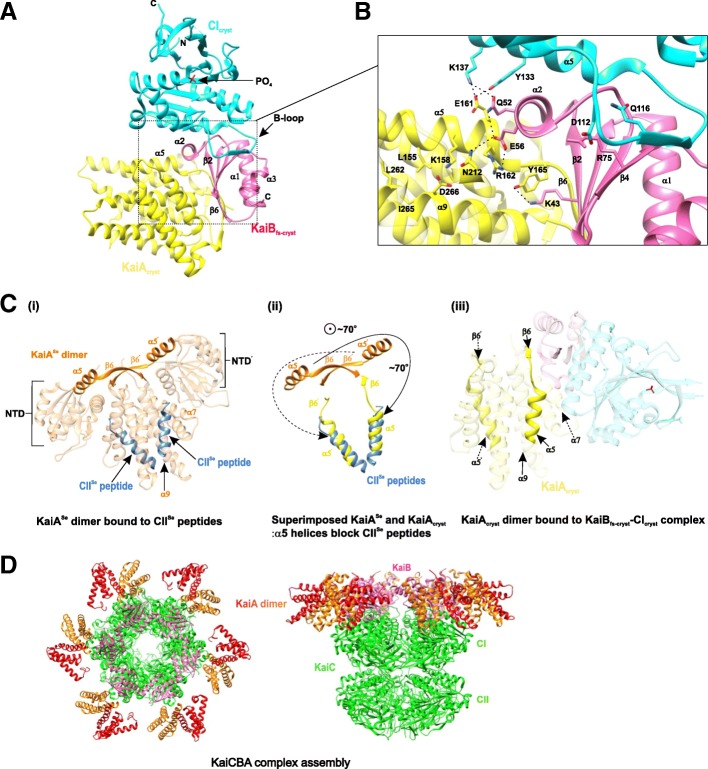
Fig. 7.
KaiCBA ternary complex depicting the KaiA autoinhibition mechanism. a A 2.6-Å ternary complex between KaiAcryst and KaiBfs-cryst–CIcryst (PDB 5JWR; KaiAcryst in yellow, KaiBfs-cryst in pink, and CIcryst in cyan). b Enlarged view of the enclosed box in a depicting the binding interface of the ternary complex. Dashed lines show the electrostatic interactions. c Conformational changes in the KaiA dimer when sequestered into a KaiCBA complex. (i) Structure of KaiA in orange bound to CII peptides in blue (from S. elongates; PDB 5C5E) highlighting the α5 and α5’ helices and β6 and β6’ strands of the two KaiA monomers. (ii) KaiASe (orange) and KaiAcryst in ternary complex (yellow) superimposed showing only the α5 and α5’ helices and β6 and β6’ strands. (iii) The CIcryst–KaiBfs-cryst–KaiAcryst ternary complex. Panels (i), (ii), and (iii) highlight only the α5 and α5’ helices and β6 and β6’ strands of the two KaiA monomers depicting the structural basis of the mechanism of KaiA autoinhibition. d Top and side views of higher KaiCBA complex assembly (PDB 5N8Y) depicting the KaiC hexamer in green, the hexameric ring of KaiB monomers in pink, and KaiA homodimers in red and orange